“Pyrroloquinoline quinone, or PQQ, is a natural antioxidant found in soil and many foods and enriched in human breast milk,” says a study lead by Karen Jonscher, PhD, an associate professor of anesthesiology and a physicist at CU Anschutz. PQQ is thought to have an essential role in the growth of new mitochondria (mitochondrial biogenesis). Studies indicate that as the number of healthy and functioning mitochondria in our cells increase, so does overall health and longevity.

This antioxidant has been observed to protect against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in the offspring of obese mice, according to researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus. The study, published online last week in the Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, is the first to demonstrate that PQQ can protect offspring of obese mothers from acceleration of obesity-induced liver disease.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the build up of extra fat in liver cells that is not caused by alcohol. It is normal for the liver to contain some fat. However, if more than 5% – 10% percent of the liver’s weight is fat, then it is called a fatty liver (steatosis).
NAFLD is part of the metabolic syndrome characterized by diabetes, or pre-diabetes (insulin resistance), being overweight or obese, elevated blood lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides, as well as high blood pressure.
NAFLD Symptoms.
Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, weight loss, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, spider-like blood vessels, yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), itching, fluid build up and swelling of the legs (edema) and abdomen (ascites), and mental confusion.

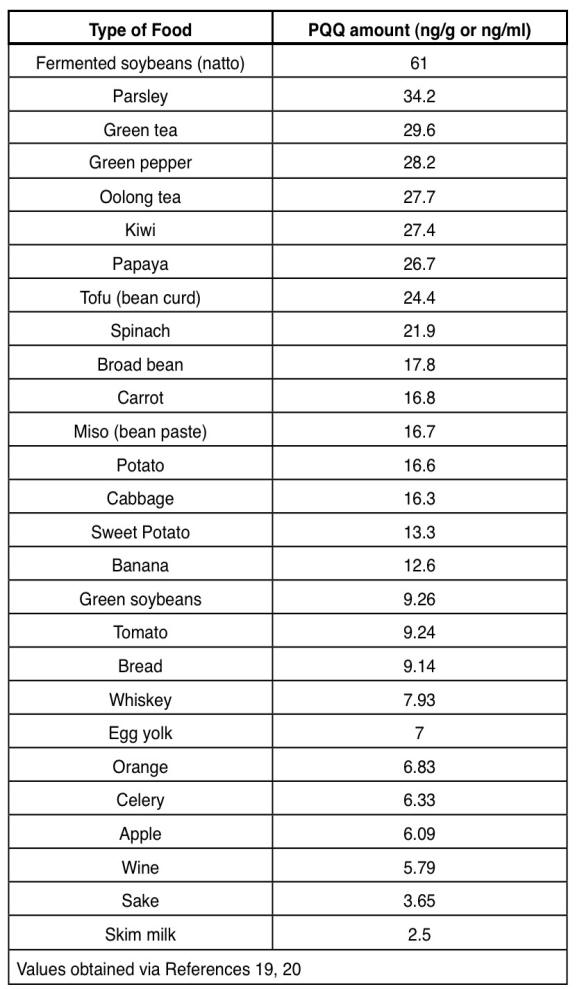
Sources of PQQ
PQQ is found in
- Human breast milk
- Soy
- Parsley
- Celery
- Kiwi
- Papaya.
It’s also found in soil and interstellar dust.
Intake:
The recommended dietary allowance of PQQ currently stands at 75 to 90 milligram per day (for adults, excluding pregnant and lactating women) for optimal function, and even higher amounts are required for clinical applications. The current recommendation of 10 to 20 mg of PQQ daily is based upon the equivalent dose in animals which has consistently improved various mitochondrial functions. There are also some clinical and observational studies that justify the dosage, especially the 20 mg dosage for enhancing memory.
Based upon the current research there is no question that it plays a critical role in human nutrition.
Disclaimer
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.