Chronic, constant stress can increase lifetime risk of heart disease and stroke, but a new survey from the American Heart Association, a global force for longer, healthier lives for all, reveals regular mealtime with others could be a simple solution to help manage stress. Of the 1,000 U.S. adults nationwide surveyed in September 2022 for the American Heart Association's … [Read more...]
Cardiovascular Health

Better Screening Could Predict and Prevent Sudden Cardiac Death in Young People
Nearly nine in ten cases of sudden cardiac death (SCD) due to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) in young people are preceded by symptoms, ECG abnormalities or a positive family history, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Erik Börjesson of Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Sweden, and colleagues. Those findings suggest that … [Read more...]
Benefits of Statin Therapy Highlighted
Stopping statin treatment early could substantially reduce lifetime protection against heart disease since a large share of the benefit occurs later in life. That's the finding of a modelling study presented at ESC Congress 2022.1 Lead author Dr. Runguo Wu of Queen Mary University of London, UK said: "The study indicates that people in their 40s with a high likelihood of … [Read more...]
Daily Avocados Improve Diet Quality, Help Lower Cholesterol Levels, Study Finds
Eating one avocado a day for six months was found to have no effect on belly fat, liver fat or waist circumference in people with overweight or obesity, according to a new study. However, it did lead to a slight decrease in unhealthy cholesterol levels. In the randomized trial, the team -- including Penn State researchers -- also found that participants who ate avocados had … [Read more...]
About 3 Grams a Day of Omega-3 Fatty Acids may Lower Blood Pressure, More Research Needed
About 3 grams daily of omega-3 fatty acids, consumed in foods or supplements, appears to be the optimal daily dose to help lower blood pressure, according to a research review published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access, peer-reviewed journal of the American Heart Association. Omega-3 fatty acids docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and … [Read more...]
Obesity Significantly Increased Heart Failure Risk Among Women with Late Menopause
A woman's body produces less estrogen and progesterone after menopause, changes that can increase the risk for cardiovascular diseases including heart failure, according to the American Heart Association. Menopause typically occurs between the age of 45 and 55, however, the average age for natural menopause has increased by 1.5 years over the past six decades, according to some … [Read more...]
Exercise Holds Even More Heart Health Benefits for People with Stress-Related Conditions
The research findings add to mounting evidence that exercise improves cardiovascular health by helping to activate parts of the brain that counteract stress. Overall, the study found that people who achieved the recommended amount of physical activity per week were 17% less likely to suffer a major adverse cardiovascular event than those who exercised less. These benefits were … [Read more...]
COVID-19 Infection Linked to Higher Risk of Neuropathy
In a study of more than 1,500 people who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 during the first year of the pandemic, the researchers found that those who tested positive for the virus were about three times more likely to report pain, numbness or tingling in their hands and feet as those with negative tests. The findings are reported online March 24 in the journal Pain. "Several … [Read more...]
Only Alcohol — Not Caffeine, Diet or Lack of Sleep — Might Trigger Heart Rhythm Condition
New research from UC San Francisco that tested possible triggers of a common heart condition, including caffeine, sleep deprivation and sleeping on the left side, found that only alcohol use was consistently associated with more episodes of the heart arrhythmia. The authors conclude that people might be able to reduce their risk of atrial fibrillation (AF) by avoiding … [Read more...]
Night Shift Work is linked to Increased Risk of Heart Problems
People who work night shifts are at increased risk of developing an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation (AF), according to research published in the European Heart Journal. The study is the first to investigate the links between night shift work and AF. Using information from 283,657 people in the UK Biobank database, researchers found … [Read more...]
Blood Clotting may be the Root Cause of Long COVID Syndrome, Research Shows
New evidence shows that patients with Long COVID syndrome continue to have higher measures of blood clotting, which may help explain their persistent symptoms, such as reduced physical fitness and fatigue. The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Previous work by the same … [Read more...]
Soft Skin Patch could Provide Early Warning for Strokes, Heart Attacks
Engineers at the University of California San Diego developed a soft and stretchy ultrasound patch that can be worn on the skin to monitor blood flow through major arteries and veins deep inside a person's body. Knowing how fast and how much blood flows through a patient's blood vessels is important because it can help clinicians diagnose various cardiovascular conditions, … [Read more...]
The Southern Diet – Fried Foods and Sugary Drinks – May Raise Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death
Regularly eating a Southern-style diet may increase the risk of sudden cardiac death, while routinely consuming a Mediterranean diet may reduce that risk, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association. The Southern diet is characterized by added fats, fried foods, eggs, … [Read more...]
Map of Metabolic Changes after Heart Attack Holds Clues to Recovery
Researchers have mapped out the changes in metabolism that occur after a heart attack, publishing their findings today in the open-access eLife journal. Their study in mice reveals certain genes and metabolic processes that could aid or hinder recovery, and might be good targets for treatments to prevent damage after a heart attack. "Although some studies have looked at … [Read more...]
More Belly Weight Increases Danger of Heart Disease even if BMI does not Indicate Obesity
People with abdominal obesity and excess fat around the body's mid-section and organs have an increased risk of heart disease even if their body mass index (BMI) measurement is within a healthy weight range, according to a new Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association published today in the Association's flagship journal, Circulation. "This scientific … [Read more...]
The right ‘5-a-day’ mix is 2 fruit and 3 vegetable servings for longer life
Studies representing nearly 2 million adults worldwide show that eating about five daily servings of fruits and vegetables, in which 2 are fruits and 3 are vegetables, is likely the optimal amount for a longer life, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation. Diets rich in fruits and vegetables help reduce … [Read more...]
Hydrogel Injection may change the way the heart muscle heals after a heart attack
Researchers at CÚRAM, the SFI Research Centre for Medical Devices based at National University of Ireland Galway, and BIOFORGE Lab, at the University of Valladolid in Spain, have developed an injectable hydrogel that could help repair and prevent further damage to the heart muscle after a heart attack. The results of their research have just been published in the journal … [Read more...]
Healthy Muscles: a Carrot on a String for Healthy Lungs
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease caused by long-term inhalation of harmful gases such as cigarette smoke. Scientists have recognized deterioration of muscle tissue, known as, as a secondary effect of damaged lungs. This frailty makes it difficult for individuals to move around and exercise, which is turn worsens the state of their lungs, causing an … [Read more...]
Three reasons why COVID-19 can cause silent hypoxia
Scientists are still solving the many puzzling aspects of how the novel coronavirus attacks the lungs and other parts of the body. One of the biggest and most life-threatening mysteries is how the virus causes "silent hypoxia," a condition when oxygen levels in the body are abnormally low, which can irreparably damage vital organs if gone undetected for too long. Now, thanks to … [Read more...]
New diagnostic test for heart failure patients could also help COVID-19 patients
A new blood test that reliably predicts outcomes for heart failure patients could lead to new diagnostics and treatments for COVID-19 patients as well, according to newly published research from cardiologists at the University of Alberta. The researchers examined circulating angiotensin peptide levels in the blood of 110 people who were experiencing heart failure due to a … [Read more...]
Fantastic muscle proteins and Where to find Them
Researchers at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) developed a mouse model that enables them to look inside a working muscle and identify the proteins that allow the sarcomere to contract, relax, communicate its energy needs, and adapt to exercise. Specifically, they were able to map proteins in defined subregions of the sarcomere, … [Read more...]
Disrupted sleep increases the risk of cardiovascular disease by promoting inflammation
Sleep disruption has been shown to be associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis, but the mechanism has been unclear. A new study in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Raphael Vallat, Vyoma Shah, and Matthew Walker of the University of California at Berkeley and colleagues reveals that fragmented sleep exacerbates atherosclerosis and may raise the risk of stroke … [Read more...]
Drinking sugary drinks daily may be linked to higher risk of CVD in women
Drinking one or more sugary beverages a day was associated with a nearly 20% greater likelihood of women having a cardiovascular disease compared to women who rarely or never drank sugary beverages, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association. In the large, ongoing … [Read more...]
New method to grow human blood vessels
A team of researchers at the University of Minnesota Medical School recently proved the ability to grow human-derived blood vessels in a pig -- a novel approach that has the potential for providing unlimited human vessels for transplant purposes. Because these vessels were made with patient-derived skin cells, they are less likely to be rejected by the recipient, helping … [Read more...]
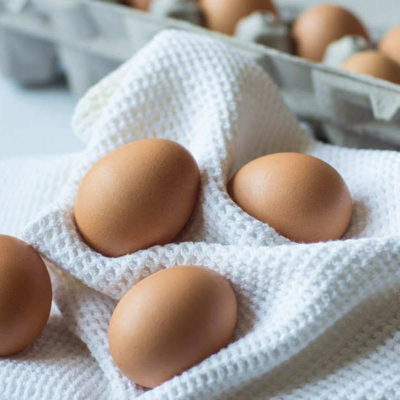
Moderate egg consumption not associated with higher cardiovascular disease risk
The relationship between egg consumption and CVD risk has been a topic of intense debate in the scientific community in recent decades. Just in the past 12 months, three published studies have reported conflicting results. The new findings update a 1999 study -- the first major analysis of eggs and cardiovascular disease -- that found no association between eggs and CVD … [Read more...]
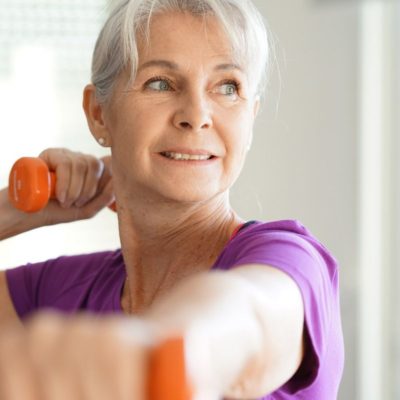
For older adults, more physical activity could mean longer, healthier lives
Two studies demonstrate that older adults may be able to live longer, healthier lives by increasing physical activity that doesn't have to be strenuous to be effective, according to preliminary research presented at the American Heart Association's Epidemiology and Prevention | Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health Scientific Sessions 2020. The EPI Scientific Sessions, March 3-6 … [Read more...]
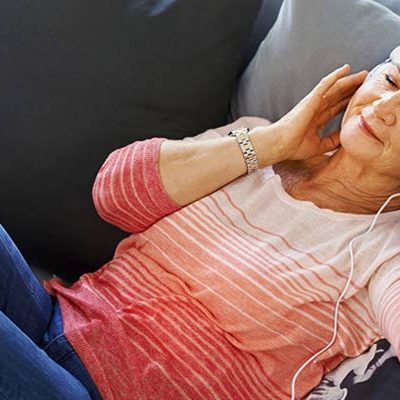
Music Therapy helps Stroke Patients
New research has found that music therapy sessions have a positive effect on the neurorehabilitation of acute stroke patients, as well as their mood. The study -- the first large-scale investigation into the feasibility of delivering these exercises -- was led by Dr Alex Street, of Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), and was carried out on a 26-bed stroke and rehabilitation unit … [Read more...]
For older adults, more physical activity could mean longer, healthier lives
Two studies demonstrate that older adults may be able to live longer, healthier lives by increasing physical activity that doesn't have to be strenuous to be effective, according to preliminary research presented at the American Heart Association's Epidemiology and Prevention | Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health Scientific Sessions 2020. The EPI Scientific Sessions, March 3-6 … [Read more...]
Drinks with added sugars linked to lipid imbalance, which increases CVD risk
Drinking 12 ounces of sugary drinks more than once per day is linked to lower levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), ("good" cholesterol), and higher levels of triglycerides, in middle aged and older adults, both of which have been shown to increase risk of cardiovascular disease. These results are from a new observational study published today in the Journal … [Read more...]
Walnuts may be Good for the Gut and Help Promote Heart Health
Walnuts may not just be a tasty snack, they may also promote good-for-your-gut bacteria. New research suggests that these "good" bacteria could be contributing to the heart-health benefits of walnuts. In a randomized, controlled trial, researchers found that eating walnuts daily as part of a healthy diet was associated with increases in certain bacteria that can help promote … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 35
- Next Page »