In many cultures, it is common to burn incense for religious and cultural practices, including meditations, celebrations and spiritual and ancestral worship. A new medically challenging case being presented at this year's American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting in Boston warns that, for those with allergies and asthma, health … [Read more...]
Study reveals that sleep prevents unwanted memories from intruding
The link between poor sleep and mental health problems could be related to deficits in brain regions that keep unwanted thoughts out of mind, according to research from the University of East Anglia (UEA). Sleep problems play an important role in the onset and maintenance of many mental health problems, but the reason for this link is elusive. A new study, published in … [Read more...]
Delivering Medicines with Microscopic Flowers
How can medicines be directed to the precise location within the body where they need to act? Scientists have been researching this question for a long time. An example would be delivering cancer drugs directly to a tumour so that they only take effect at this specific location, without causing side effects in the rest of the body. Research is under way to identify carrier … [Read more...]
Newer Epilepsy Medications used during pregnancy do not affect neurological development in children
"Controlling seizures during pregnancy is an important part of prenatal care for women with epilepsy, but for years, the effects of newer anti-seizure medications on their children was unknown," said Adam Hartman, M.D., program director at NIH's National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). "One major component of this study was correlating the cognitive … [Read more...]
Cancer Risk Declines in old age, Research Helps Explain why
When it comes to cancer, aging is a double-edged sword, researchers are increasingly learning. Age is considered the most important risk factor for cancer. That's because genetic mutations build up in cells over years and decades, and ultimately drive the development of cancer. Now a study from researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) and their … [Read more...]
Tiny, Daily Bursts of Vigorous Incidental Physical Activity could Almost Halve Cardiovascular Risk in Middle-Aged Women
An average of four minutes of incidental vigorous physical activity a day could almost halve the risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks, for middle-aged women who do not engage in structured exercise, according to new research from the University of Sydney, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine. "We found that a minimum of 1.5 minutes to … [Read more...]
Cancer ‘Fingerprint’ can Improve Early Detection
Different types of cancer have unique molecular 'fingerprints' which are detectable in early stages of the disease and can be picked up with near-perfect accuracy by small, portable scanners in just a few hours, according to a study published today in the journal Molecular Cell. The discovery by researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona sets the … [Read more...]
Short-Term Cognitive Boost From Exercise May Last For 24 hours
The short-term boost our brains get after we do exercise persists throughout the following day, suggests a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers. Previous research in a laboratory setting has shown that people's cognitive performance improves in the hours after exercise, but how long this benefit lasts is unknown. The new study, published in the … [Read more...]
Eating Dark Chocolate Linked with Reduced Risk of Type 2 diabetes
Consuming dark, but not milk, chocolate may be associated with lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes (T2D), according to a new study from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. "Our findings suggest that not all chocolate is created equal," said lead author Binkai Liu, doctoral student in the Department of Nutrition. "For anyone who loves chocolate, this is a … [Read more...]
Keeping a Longer Overnight Fast and Eating an Early Breakfast may be Associated with a Lower Body Mass Index
According to a study published in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, there are two specific habits that are associated with a lower body mass index (BMI) in the long term: keeping a longer overnight fast and eating breakfast early. This research was led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la … [Read more...]
Should Men and Women Eat Different Breakfasts to Lose Weight?
It's not a bad thing if you pick a toasted bagel for breakfast, while your partner chooses eggs. In fact, according to a new study from the University of Waterloo, that difference could help you lose some weight. The study, which employed a mathematical model of men's and women's metabolisms, showed that men's metabolisms respond better on average to a meal laden with high … [Read more...]
Season of Birth is Associated With the development of asthma and allergic rhinitis
Season of birth, and specifically being born in autumn or winter, is associated with allergic rhinitis and asthma in Finland, a new study by the University of Eastern Finland, the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital shows. Conversely, being born in summer was associated with the lowest incidence of asthma and allergic rhinitis. "When using summer as … [Read more...]
Invention Quickly Detects Earliest Sign of Heart Attack
"Heart attacks require immediate medical intervention in order to improve patient outcomes, but while early diagnosis is critical, it can also be very challenging -- and near impossible outside of a clinical setting," said lead author Peng Zheng, an assistant research scientist at Johns Hopkins University. "We were able to invent a new technology that can quickly and accurately … [Read more...]
The Secret to Losing Weight could All be Down to a Combination of 14 ‘Skinny Genes’, a New Study has Found.
University of Essex researchers discovered they helped people drop twice as much weight when they ran for half an hour three times a week. The team -- led by Dr Henry Chung, from the School of Sport, Rehabilitation and Exercise Sciences -- found those with more of the genes slimmed the most across eight weeks. People with the most markers lost up to 5kg during the study … [Read more...]
How Your Skin Tone Could Affect Your Meds
Skin pigmentation may act as a "sponge" for some medications, potentially influencing the speed with which active drugs reach their intended targets, a pair of scientists report in a perspective article published in the journal Human Genomics. The researchers argue that a sizable proportion of drugs and other compounds can bind to melanin pigments in the skin, leading to … [Read more...]
Excess Body Weight Tied to Increased Risk for Second Cancers
Cancer survivors who had overweight or obesity at the time of their initial cancer diagnosis have a higher risk for a second primary cancer, particularly an obesity-related cancer, a new analysis found. Cancer survivors have an increased risk for another primary cancer. Studies suggest that lifestyle factors, such as excess body weight, may contribute to the risk for a … [Read more...]
Time For US-India Collaboration For Mental Health: US Surgeon General
Now is the time for the United States of America and India to collaborate to tackle the global mental health crisis we are witnessing today, United States Surgeon General Dr Vivek Murthy said at a press conference in the city recently. Dr Murthy is the first Surgeon General of Indian descent. As the Co-Chair of the World Health Organization’s Commission on Social … [Read more...]
Time-Restricted Eating May Help Adults With Metabolic Syndrome Improve Several Health Markers
Adults with metabolic syndrome and elevated blood sugar levels who eat within a time-restricted window may experience modest improvements in several measures, including A1c levels, weight, and body fat, according to a randomized controlled trial published in Annals of Internal Medicine. For the study, participants kept to an 8- to 10-hour window of eating, a dietary … [Read more...]
Frequent Fizzy or Fruit Drinks and High Coffee Consumption Linked to Higher Stroke Risk
Frequent drinking of fizzy drinks or fruit juice is associated with an increased risk of stroke, according to new findings from global research studies co-led by University of Galway, in collaboration with McMaster University Canada and an international network of stroke researchers. The research also found that drinking more than four cups of coffee per day also increases … [Read more...]
One in Three Americans has a Dysfunctional Metabolism, but Intermittent Fasting could help
More than one-third of adults in the United States have metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that significantly raise a person's risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, excess abdominal fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels. In a new clinical trial, researchers at the Salk Institute and … [Read more...]
Sport-Related Stress may Affect Whether College Athletes eat Enough Calories
Studies have long shown that unhealthy attitudes about eating -- like desiring a thinner body or deliberately restricting caloric intake -- can lead to the underconsumption of nutrients, the team said. College athletes may face pressures to maintain specific body types for competitive reasons, so they can be especially vulnerable to these phenomena, according to the … [Read more...]
New Blood Test Could be an Early Warning for Child Diabetes
New study from King's College London published in Nature Medicine reveals a new relationship between lipids and diseases impacting metabolism in children, which could serve as an early warning system for conditions like liver disease. Using machines that test blood plasma in babies that already exist in hospitals, the researchers suggest this could help doctors spot early … [Read more...]
Study Proposes New Heart Failure Treatment Targeting Abnormal Hormone Activity
In heart failure, which is considered a global pandemic, the heart can no longer pump blood effectively. In HFpEF, the heart can pump normally but its muscles are too stiff to relax to re-fill the chambers with blood properly. It is often seen in older adults and people with multiple risk factors including high blood pressure (hypertension), obesity and diabetes. They … [Read more...]
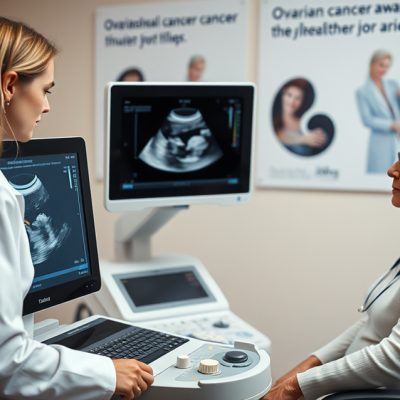
Most Accurate Ultrasound Test could Detect 96% of Women with Ovarian Cancer
An ultrasound test that detected 96% of ovarian cancers in postmenopausal women should replace current standard of care test in the UK according to a new study. In a paper published in Lancet Oncology today (Monday 30 September), research funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) and led by Professor Sudha Sundar from the University of Birmingham … [Read more...]
New Therapeutic Approach to Preventing Cancer From Spreading to the Brain
Researchers at McMaster University have identified a new therapeutic approach to preventing cancer from spreading to the brain. In a new study, published recently in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, researchers Sheila Singh and Jakob Magolan discovered a critical vulnerability in metastatic brain cancer, which they say can be exploited with new drugs to prevent … [Read more...]
Games, Puzzles and Reading can Slow Cognitive Decline in the Elderly — Even in Those with Mild Cognitive Impairment
The aging process can lead to diminished cognitive functioning for older adults. In addition, about 10 percent of people previously diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment develop Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia every year. Although a few studies have found that activities such as putting together jigsaw puzzles can protect against cognitive aging, the … [Read more...]
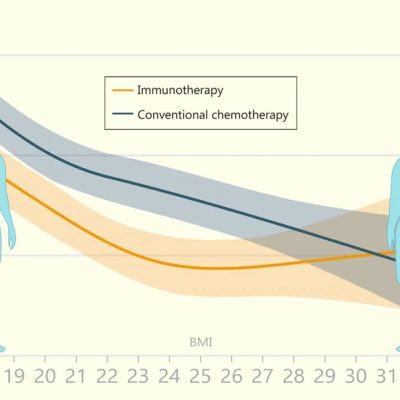
BMI’s Relation to Cancer Therapy Mortality Risks Not so Straightforward
While being overweight increases the risk of developing lifestyle-related diseases, there is a phenomenon known as the obesity paradox where a decreased risk of death has been seen during cancer therapy. However, that paradox might not be the trend for all cancer therapies, an Osaka Metropolitan University team reports in JAMA Network Open, a publication of the American Medical … [Read more...]
Like Father, Like Daughter
When they become fathers, men who have an unhealthy, high-cholesterol diet can cause increased risk of cardiovascular disease, or CVD, in their daughters, a University of California, Riverside-led mouse study has found. The research, published in the journal JCI Insight, is the first to demonstrate this result seen only in female offspring. CVD, the leading cause of death … [Read more...]
Excessive Light Pollution May Increase Risk of Alzheimer’s, Especially in Younger People
In some places around the globe, the lights never go off. Streetlights, roadway lighting, and illuminated signs can deter crime, make roads safer, and enhance landscaping. Undisrupted light, however, comes with ecological, behavioral, and health consequences. In the US, some states have legislation in place to reduce light pollution; however, levels of light at night remain … [Read more...]
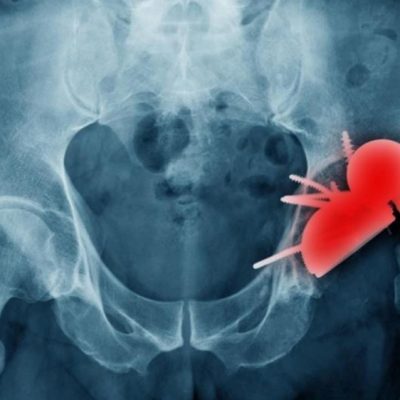
Infections Following Hip Replacement Associated with an Increased Risk of Death, Study Finds
Patients who develop a periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) after a total hip replacement have more than a five-fold increased risk of mortality within 10 years, according to new research published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. In one of the largest studies to date of patients with PJI after total hip arthroplasty (THA), researchers from ICES, Sunnybrook Research … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 424
- Next Page »