|
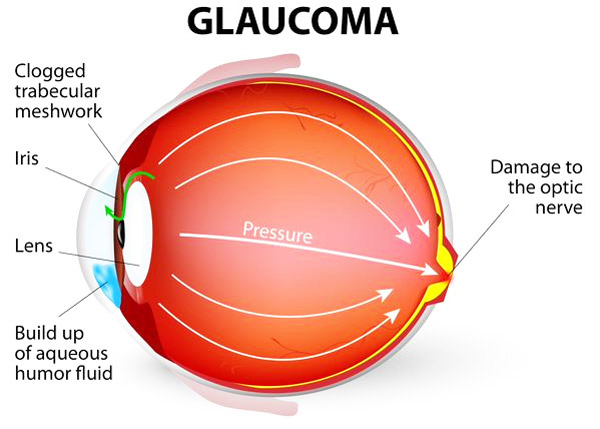
A normal, healthy eye is nourished and protected by fluid, which, just like your blood, has pressure. Glaucoma is a condition that results in damage to the optic nerve, which carries images from the eye to the brain when the eye pressure rises to a dangerous level. This damage can reduce your vision and even cause blindness.
Glaucoma can occur in one to four main forms.
|
|
Glaucoma is the third most common cause of blindness in the U.S. Chronic Glaucoma develops gradually as you age .Unless you have a regular eye examination that includes a test for Glaucoma you may not realize you have a problems until the disease has caused considerable injury and your sight is affected.Damage caused by Glaucoma is irreversible but if the condition is detected early and treated the harmful buildup of pressure inside the eye can be prevented. For this reasons your eyes should be tested for Glaucoma every year after age 40. You are more likely to develop chronic Glaucomaif you are over 40, black, have a family history of Glaucoma are a nearsighted or have diabetes.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chronic Glaucoma develops very slowly. Most people have no symptoms until the disorders has damaged the optic nerve and impaired their visions. Chronic Glaucoma is usually detected during a regular eye examination by an ophthalmologist. By contrast acute Glaucoma occurs suddenly and requires immediate medical attention to reduce the buildup of pressure inside the eye. Acute Glaucoma may cause symptoms such as blurred visions, severe eye pain, a headache, rainbow halos around the cornea, nausea or vomiting. |
Unlike chronic Glaucoma which usually causes no symptoms until your visions is impaired acute Glaucoma occurs suddenly. Acute Glaucoma requires emergency medical treatment to save your vision. If any of the following symptoms occur suddenly call your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room
|
|
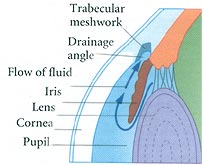
Your ophthalmologist can examine yours eyes and perform tests to determine if you have Glaucoma or are at risk of developing it. He or she will measure the pressure inside your eye examine the drainage angel for signs of blockage and examine yours optic nerves for signs of damage. Yours doctor may also evaluate the completeness of your visions in each to see if the disease has affected your sight.
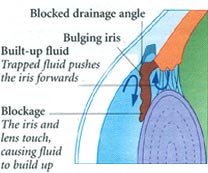
Your ophthalmologist will also look into your eye through the cornea to evaluate the depth of the front of your eyeball. A shallow or narrow drainage angel suggests that the drainage of fluid from the eye may eventually that can lead to acute closed angel Glaucoma. Confrontation visual field exam may also be conducted which is a quick and basic evaluation of the visual field done by an examiner sitting directly in front of you. With one eye covered, you are asked to look at the examiner’s eye and tell when you can see the examiners hand. To evaluate the health of the optic nerve the doctor may use a hand held viewing instrument called an ophthalmoscope which has a very bright light to look through your pupil. The optic nerve located in the back of your eye transits images from the eye to your brain. Glaucoma can cause irreversible damage to this nerve which can lead to blindness. Your doctor may want to test the visual field of each eye to determine if your sight has been affected by Glaucoma. To do this he or she will move an object such as a pencil into your view form the side while your look straight ahead. If you cannot see the object until it is almost directly in front of your peripheral vision may have been impaired by Glaucoma. If your doctor suspects your have Glaucoma he or she is likely to recommend additional tests including gonioscopy to examine the drainage angle of your eye. This lens has mirrors and facets that enable the doctor to view the drainage angle and look for any changes or signs of blockage. Your eye will first be numbed with anesthetic drops to reduce any discomfort during the procedure. Your doctor may also use a special camera to take photographs of each optic nerve. These pictures are used to document and monitor any changes in or damage to the nerves. |
The whole purpose of treatment for Glaucoma is to prevent further loss of vision. Once the nerve cells have been damaged and the vision carried by those nerve cells lost, they cannot be replaced. LOSS OF VISION IN Glaucoma IS IRREVERSIBLE. Lowering the intraocular pressure (IOP) will not restore lost vision, but is an attempt to prevent further vision from being lost. The only treatment which has so far been proven to be effective remains lowering IOP. This again requires chronic use of medications. Administration of anti-Glaucoma drops and its spacing should be followed under the strict guidance of an ophthalmologist. Some patients might experience side effects, such as redness and allergy.
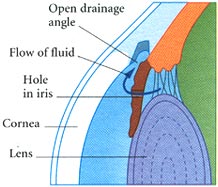
Medications If your have Glaucoma your doctor will first prescribe medication in the from of eye drops. This medication decrease pressure inside the eye either by slowing the amount of fluid produced in the eye or by improving the flow of fluid out of the eye . You must take the eye drops regularly usually several times a day for the rest of your life to prevent damage from Glaucoma and to preserve your visions . Xalatan (latanaprost), Alphagan (brimonidine) and Trusopt (dorzolamide) are examples of these new drugs. Do not stop taking the drops because the medication is effective in preventing Glaucoma only for as long as you use it. Tell your doctor if you experience and side effects from the eye drops which may include a stinging sensation in your eyes redness in your eyes blurred visions or irregular heartbeat. In some cases the does of medication can be adjusted to reduce these side affects. Medications taken in form of pills can also reduce pressure inside the eye. However because this medications may have more serious side affects than the eye drops it is used only if eye drops have not been effective. Side effects of the pills may include tingling of your fingers and toes, drowsiness, loss of appetite, constipation, kidney stones, or reduced ability of your blood to clot. If you experience any of these side effects call your ophthalmologist immediately. He or she may be able to adjust the doses or prescribe a different medication. Surgery If you have acute closed angle Glaucoma or you are at risk of developing it treatment is likely to include a surgical procedure called an Iridotomy which is usually performed using laser beams which creates a tiny drainage hole in the iris. The procedure is painless takes only a few minutes and is done in the doctors or an outpatient facility.
If you have chronic prone angle Glaucoma that cannot be controlled with eye drops or pills your doctor may recommended laser surgery to create a better flow of fluid through the drainage angle. This relives the dangerous pressure inside the eye. The procedure which is painless takes a few minutes an is done in the doctor’s office or in an outpatient facility . In some cases traditional surgery in a hospital operating room may be necessary to create an opening in the front of the eye to allow excess fluid to drain out. The procedure which is done using general or local anesthesia takes about I to 1 ½ hours. Complications may include pressure inside the eye that is too high or too low or bleeding. In some cases the procedure is not effective and must be repeated. Lifestyle Modifications
Some of the vitamins and minerals important to the eye include zinc and copper, antioxidant vitamins C, E, and A (as beta carotene), and selenium, an antioxidant mineral. While no disease in humans has been proven to arise as a result of vitamin E deficiency, vitamin E added to regular Glaucoma medication improved visual fields in a majority of patients studied. Vitamin E has also shown promise in the treatment of premature retinopathy. |
|
Because the surface of your eye can hold only a limited amount of fluid when you use eye drops any excess liquid will run out of your eye . This extra fluid also pools in the corner of your eye and a small amount may even drains into your nose where it can enter your bloodstream and possibly cause side effects . In additional these medications can be expensive so you should not want to waste any. Here are some tips for taking your eye drops correctly .
|
|
Note: Untreated acute Glaucoma results in severe and permanent vision loss after the onset of symptoms. Vision can be preserved with prompt treatment. With proper care, regular eye exams, eye drops and appropriate treatment, there’s tremendous hope for maintaining your vision for a lifetime. |
Disclaimer
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
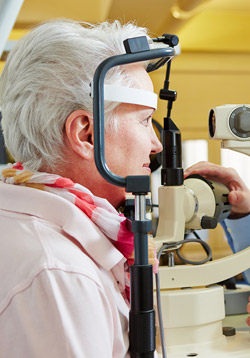 The test for measuring the pressure inside your eyes called tonometry is quick safe and painless. Your ophthalmologist will put a drop to numb it before putting in each eye. Then he or she will place an instrument called a tonometer against your
The test for measuring the pressure inside your eyes called tonometry is quick safe and painless. Your ophthalmologist will put a drop to numb it before putting in each eye. Then he or she will place an instrument called a tonometer against your 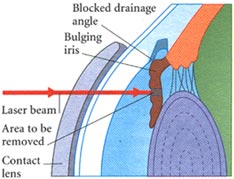
 In a recent study, it was observed that people with Glaucoma who exercised regularly for three months reduced their IOPs an average of 20%. These people rode stationary bikes 4 times per week for 40 minutes. Measurable improvements in eye pressure and physical conditioning were seen at the end of three months. These beneficial effects were maintained by continuing to exercise at least three times per week; lowered IOP was lost if exercise was stopped for more than two weeks. Regular
In a recent study, it was observed that people with Glaucoma who exercised regularly for three months reduced their IOPs an average of 20%. These people rode stationary bikes 4 times per week for 40 minutes. Measurable improvements in eye pressure and physical conditioning were seen at the end of three months. These beneficial effects were maintained by continuing to exercise at least three times per week; lowered IOP was lost if exercise was stopped for more than two weeks. Regular 


