|
|
Brow Lift
Other names for brow lift :-eyebrow lift, forehead lift, coronal lift, endoscopic brow lift, direct brow lift, temporal lift, midforehead lift,
internal brow lift, browplasty, browpexy, upper face lift.
|
Ideally, a woman's eyebrows should arch on or slightly above the
upper
orbital rims. Laughing, smiling,
crying and squinting are all everyday facial movements that gradually cause your
forehead to develop unwanted furrows, wrinkles and lines. This, coupled with the
inevitable effects of
aging can create forehead lines that lead to a tired, worn
look
Primary goal: Elevation of drooping eyebrows
Secondary
goals: Softening of forehead wrinkling and glabellar (the area between the
brows) frown lines.
|
Brow lift surgery improves the face dramatically by creating a brighter,
softer, fresher appearance. It lifts heavy eyebrows away from the eyes and
smoothes out vertical lines between the eyebrows and transverse lines across the
forehead.
|

|
|
Understanding the muscle anatomy of the eyebrow
|
|
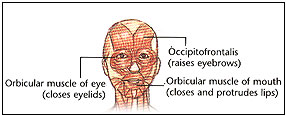 The forehead and eyebrow regions are composed of 5 major muscles: the
occipitofrontalis, orbicularis oculi, depressor superciliaris, corrugator
supercilii, and procerus. The occipitofrontalis has 4 bellies, 2 occipital and 2
frontal, connected by the epicranial aponeurosis, also termed the galea
aponeurotica. The occipital bellies arise from the highest nuchal line on the
occipital bone and pass forward to insert on the galea. The frontal portion has
no bony insertion but arises from the skin and superficial fascia of the
eyebrow, passes through the orbital orbicularis oculi muscle, and inserts on the
galea approximately midway between the coronal suture and the brow. The forehead and eyebrow regions are composed of 5 major muscles: the
occipitofrontalis, orbicularis oculi, depressor superciliaris, corrugator
supercilii, and procerus. The occipitofrontalis has 4 bellies, 2 occipital and 2
frontal, connected by the epicranial aponeurosis, also termed the galea
aponeurotica. The occipital bellies arise from the highest nuchal line on the
occipital bone and pass forward to insert on the galea. The frontal portion has
no bony insertion but arises from the skin and superficial fascia of the
eyebrow, passes through the orbital orbicularis oculi muscle, and inserts on the
galea approximately midway between the coronal suture and the brow.
The orbicularis oculi muscle has 3 parts, the orbital, preseptal, and
pretarsal orbicularis oculi muscle. The orbital portion overlies the orbital rim
and arises from the anterior limb of the medial canthal tendon and the
surrounding periosteum. The fibers sweep superiorly and inferiorly around the
eye and meet laterally over the zygoma. The preseptal portion of the orbicularis
oculi has superficial heads from the medial canthal tendon and deep heads from
the posterior lacrimal crest. The fibers that sweep laterally form the lateral
palpebral raphe.
The pretarsal fibers arise from the medial canthal tendon and Horner muscle.
These fibers pass laterally to unite at the lateral canthal tendon. The
orbicularis oculi muscle closes the eyelids, thereby pulling the skin of the
forehead, temple, and cheek toward the eyes. The superior orbital portion of the
orbicularis oculi muscle is a particularly powerful depressor of the brow, as is
evident in patients with blepharospasm.
The corrugator supercilii muscles originate from the nasal process of the
frontal bone at the superomedial orbital rim. The muscle inserts into the medial
cutaneous portion of the eyebrow, interdigitating with the frontalis muscle. The
corrugator muscles produce vertical glabellar furrows.
The procerus muscle appears as a continuation of the inferior medial end of
the frontalis muscle. It arises from the lower part of the nasal bone, and its
action pulls down the medial end of the eyebrow and produces horizontal wrinkles
of the skin.
The muscle plane of the eyebrow is secured to the frontal bone periosteum by
a firm attachment on the underside of the fat pad, often known as the deep
galeal insertion, particularly over the medial two thirds of the orbit.
|
|
|
Points to consider
|
|
Careful assessment by the surgeon is critical to ensure a satisfactory
cosmetic result.
-
Frequently, droopy eyebrows and excess eyelid skin are a combined
problem. If this is the case, simply removing some eyelid skin will not
correct the problem. In fact, it may worsen it by creating a shortage of
skin in the upper lid causing the brow to be pulled down further.
-
If both a brow lift and blepharoplasty are found to be necessary, it is
important to place the eyebrow in its correct position by performing the brow
lift surgery first. In this way, less upper eyelid skin is removed during
the blepharoplasty, thus preventing any problems with eyelid closure.
-
Brow lift surgery for forehead wrinkles is particularly effective in
correcting droopy eyebrows as well.  If, however, droopy eyebrows are not
the problem, other options may be considered, including laser resurfacing,
collagen implants or muscle relaxants such as Botox. If, however, droopy eyebrows are not
the problem, other options may be considered, including laser resurfacing,
collagen implants or muscle relaxants such as Botox.
-
A "sinking" nose and excess nasal skin can be corrected with a brow lift, as
an alternative to a rhinoplasty (nose job). Asymmetrical eyebrows, where
one side sits higher than the other, may be improved by lifting the brow on the
droopy side.
|
|
|
What is involved in a brow lift?
|
|
Many surgical approaches to the ptotic brow are available, including the
direct brow lift, mid forehead lift, pretrichial lift, temporal lift, coronal
lift, and endoscopic lift. This article discusses the assessment and planning of
brow lifts in general and the coronal technique in particular. Three surgical techniques are used,
each having distinct advantages and disadvantages:
-
The coronal technique is an incision made either in the scalp or at the
junction of the scalp hair and forehead.
-
The mid-forehead technique involves an incision made within the natural
creases of the mid-forehead.
-
The direct technique locates the incision just within the hairline of the
upper part of the eyebrow.
 The coronal technique is the most popular because the incision is hidden by
the hair. By partially removing some of the muscle as well as the
redundant skin, furrows and wrinkles on the forehead can be smoothed out as the
same time the brows are lifted. The most up-to-date method of performing the coronal technique utilizes a
laser and an endoscope. An endoscope is a small round tube or cannula
through which a light, a microscope and the fiber optics of the laser are
passed. With conventional scalpel surgery the incision is made from ear to
ear across the top of the forehead just within the hair line. The coronal technique is the most popular because the incision is hidden by
the hair. By partially removing some of the muscle as well as the
redundant skin, furrows and wrinkles on the forehead can be smoothed out as the
same time the brows are lifted. The most up-to-date method of performing the coronal technique utilizes a
laser and an endoscope. An endoscope is a small round tube or cannula
through which a light, a microscope and the fiber optics of the laser are
passed. With conventional scalpel surgery the incision is made from ear to
ear across the top of the forehead just within the hair line.
 The incision
is much smaller with the laser and endoscopic technique; 1 to 2 centimeter if
reduction of the forehead and glabellar (between the eyebrows) wrinkles is the
goal and a bit longer if a brow lift is also being performed. An improved
visual field is possible because the laser seals off the blood vessels.
The endoscope allows the surgeon to work under the skin without having to pull
the entire skin flap away from the forehead. The incision
is much smaller with the laser and endoscopic technique; 1 to 2 centimeter if
reduction of the forehead and glabellar (between the eyebrows) wrinkles is the
goal and a bit longer if a brow lift is also being performed. An improved
visual field is possible because the laser seals off the blood vessels.
The endoscope allows the surgeon to work under the skin without having to pull
the entire skin flap away from the forehead.
The mid-forehead technique reduces wrinkling on the forehead and lifts droopy
eyebrows, however, the disadvantage is that the scar is visible on the forehead.
The direct method does not reduce the wrinkles on the forehead, it is
strictly a
 technique
for lifting the brows. The surgeon can more accurately position the brow
with this method, a particularly important consideration when the brows are
asymmetrical. technique
for lifting the brows. The surgeon can more accurately position the brow
with this method, a particularly important consideration when the brows are
asymmetrical.
|
|
|
How long does brow lift surgery take and does it hurt?
|
|
The length of surgery varies with the technique being used and the extent of
the correction.
The actual surgery is painless because a local anesthetic is used to numb the
area prior to the procedure. After the freezing wears off, some discomfort
may be felt along the incision. A temporary headache and tightness of the
forehead and scalp may also be experienced. Oral painkillers are all that
is needed to relieve this discomfort, but no acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin)
products should be used.
|
|
|
When can normal activities be resumed?
|
|
With conventional surgery swelling and bruising will last approximately 7 to
10 days, whereas with the laser and endoscopic method, the recovery period is
only 3 to 4 days. Most people do not feel presentable in public until the
initial stages of swelling and bruising have passed. Elevation of the head
is recommended until the swelling has subsided. When this occurs any
normal activity which does not precipitate discomfort is allowed.
|
|
|
How will surgery affect the face?
|
|
A conventional coronal brow lift will raise the hairline and a hairstyle
change may be recommended if the change is quite dramatic. This is not as
significant a problem when the laser and endoscopic technique is used.
A softer, brighter, more alert and youthful look will be noticed after the
procedure. The appearance of the upper eyelids is also improved and the
eyes will look wider. It is not uncommon to receive compliments on a
well-rested happy look after brow lift surgery.
|
|
|
|
How long does the result last?
|
|
Brow lift surgery does not prevent aging. Lines of expression over the
forehead and between the eyebrows will still be present, although to a much
lesser extent. With time, they become more pronounced but the youthful
effect created by the surgery remains for a prolonged period of time.
|
|
|
What are the possible complications of a brow lift?
-
Prolonged Redness of the Scar:
This is unusual and of significance only in cases where the incision has been
made in the forehead. The scar may also be tender and lumpy.
Eventually this subsides but it may take 1 to 2 years. The vascular lasers
(pulsed dye or variable pulse width) can be used to remove the redness.
Injections of cortisone and resurfacing with the carbon dioxide laser can smooth
out raised and uneven scar tissue. Medications and ointments are not
effective in speeding up the healing process. Makeup can be used to
camouflage a scar until it has healed.
-
Balding:
Women, with male-pattern
hair loss or a strong family
history of balding are cautioned about scarring. As balding progresses, a
scalp scar will become more and more apparent because it is no longer hidden
within the hair. A scalp incision often accelerates hair loss because of
the tension of the scar and the subsequent interruption of the blood supply to
the scalp. Other causes of hair loss in the region of the scar are
infection and hematoma, both of which are rare. This is much less of a
problem with the laser and endoscopic technique.
-
Loss of Sensation:
Often, a transient loss of sensation over the forehead and scalp to the crown
of the head is felt. Feeling returns to the forehead within 4 to 6 weeks
and to the scalp after 6 to 9 months. The smaller incisions used
with the laser and endoscopic technique significantly reduce the occurrence of
this complication.
-
Overcorrection:
If too much skin is removed, the face may look surprised or startled.
With time, gravity's effect will improve this result. Overcorrection by
too much tension at the scalp incision. This may cause poor healing, a
wide scar, and hair loss.
-
Itching:
This may be troublesome, especially in the scalp area behind the incision.
Fortunately this eventually subsides as the incision heals.
-
Muscle Weakness:
Muscle weakness is usually a temporary condition which gradually
disappears. A positive aspect of this is that the forehead furrows
markedly diminish with relaxed muscles.
|
|
|
What are the alternatives to brow lift surgery?
|
|
Collagen implants or muscle relaxants are alternatives to brow lift surgery
for deep furrows on the forehead. Droopy eyebrows, however, require some
form of surgery. Laser resurfacing of the forehead may tighten the skin
above the brow enough to give droopy eyebrows a bit of a lift. If the
eyebrows are really heavy then a brow lift is the only option available.
Related Links
|
|
|
|
|
|









