Although labor and delivery usually proceed smoothly, unanticipated problems sometimes develop. Hospitals are well equipped to deal with these complications. At the same time, it is important to be aware of the warning signs of possible complications so you can alert your doctor immediately of any problems. All, through the week, WF experts will cover a series on problems that can occur during labor and delivery.
During pregnancy, the developing baby is protected by a fluid-filled sac called the bag of waters, or the “membranes.” This bag usually stays intact until several hours before labor starts-or even for a while after labor has begun-but it can burst or start leaking any time during the pregnancy. Once the membranes rupture, labor usually starts within 12 to 24 hours. If labor doesn’t begin during this period, the situation is called premature rupture of membranes (PROM).
For most women if the amniotic membranes rupture (the water breaks) early, labor follows within a few hours.
Causes
Conditions that most often cause the premature rupture of membranes include:
- Infections of the uterus- Maternal infection is probably the most common risk of PROM. Ironically, this complication is the one most likely to be caused by the doctor and hospital environment.
At all gestational ages, patients who have had only a sterile speculum exam have an average of 11.3 days of latency; whereas those who have had digital vaginal exams only last 2.1 days before labor starts . Obviously, the risk to the premature fetus is lessened with each day it can remain in the womb, making digital exams a definite risk to the baby. - Multiple births-(twins, triplets, etc)
- In-competent cervix – During normal labor, the cervix opens (dilates) to allow the fetus to pass through the vagina during delivery. An incompetent cervix gradually opens due to the pressure from the developing fetus after about the 13th week of pregnancy. The cervix begins to thin out and widen without any contractions or labor. The membranes surrounding the fetus bulge down into the opening of the cervix until they break, resulting in the loss of the baby or a very premature delivery.
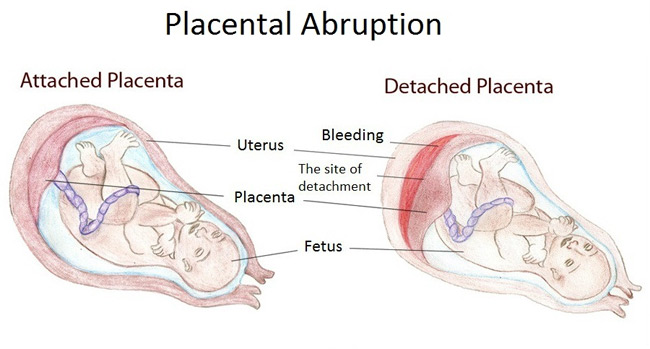
- Premature separation of the placenta (placental abruption). – occurs when the placenta that is implanted normally inside the uterus separates prematurely from the wall of the uterus, during the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios)
- Smoking is also a risk factor- Studies have also found the risk of PROM increased with the number of cigarettes the mother smoked, regardless of alcohol and caffeine intake.
- Certain procedures carry an increased risk of PROM, including amniocentesis and cervical cerclage.
Signs/Symptoms
If your membranes rupture, you are likely to feel a gush or trickle of fluid out of your vagina. (Sometimes, a woman thinks her membranes have broken when in fact urine has been pushed out by the weight of the baby on her bladder) Your doctor can tell in a pelvic examination. He or she will take a sample of the fluid in your vagina and have it tested to determine whether your bag of waters has broken. if your membranes have ruptured and if your cervix has started to thin (efface) or open (dilate). He or she may also take samples of amniotic fluids to evaluate the maturity of the baby’s lungs and to check for infections.
Treatment
Specific treatment for PROM will be determined by your physician based on:
- your pregnancy, overall health, and medical history
- extent of the condition
- your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies
- expectations for the course of the condition
- your opinion or preference

General Care
- Hospitalization is normally required for further diagnostic studies and to make determinations about treatment and delivery.
- If the membranes rupture after the 36th week of pregnancy, labor usually begins in 24 to 48 hours. If it does not labor will probably be induced. The risk of infections begins to increase 24 hours after the membranes rupture. Because of the risk of infections you should not have intercourse or put anything into your vagina, including tampons.
- Although rare the membranes can rupture before the 25th week of pregnancy. When the membranes rupture this early in pregnancy, a doctor will try to delay the onset of labor for as long as it is safe for the baby. The woman is usually admitted to the hospital so that her temperature and the baby’s heart rate can be monitored continuously, an increase in either may be an indications that an infections is developing inside the uterus. Exposure to infections inside the uterus can significantly reduce a baby’s chances of survival.
Only one fourth of babies born before the 25th week of pregnancy survive outside the uterus. Because they are not fully developed at birth, those that do survive may have permanent disabilities including slow development, mental retardations inadequate development of their lungs or blindness. - On rare occasions, the leakage will cease, and the membranes are said to “seal over.” The amniotic fluid re-accumulates.
Call Your Doctor If…
- You have a high temperature.
- You are having contractions.
- Your baby does not move very frequently in 24 hours.
Medication
- Tocolytics – medications used to stop preterm labor.
- Oxytocin may be used to induce labor.
- Antibiotics, if an intrauterine infection is present, and sometimes as an infection prevention therapy while awaiting spontaneous labor. Steroids may be prescribed prior to delivery in some cases to enhance fetal pulmonary maturity.
- If the doctor prescribes medicine, take it exactly as directed. If you feel it is not helping, tell the doctor, but do not quit taking it on your own.
Only the fourth of babies born before the 25th week of pregnancy survive outside the uterus. Because they are not fully developed at birth, those that do survive may have permanent disabilities, including slow development, mental retardation, inadequate development of their lungs, or blindness.

Activity
Bed rest while awaiting labor and delivery. You may be allowed some walking around with medical approval. The hospital can cause a lot of stress. Try controlling it through such methods as deep breathing, muscle relaxation, meditation, or biofeedback. If you feel anxious and worried, try talking about it. Sharing can help.
Diet
No special diet unless labor and delivery are immediate.
Prevention
Unfortunately, there is no way to actively prevent PROM. However, this condition does have a strong link with cigarette smoking and mothers should stop smoking as soon as possible.
Disclaimer
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.