 Worldwide, there are about 2 billion people suffering from various types of life threatening diseases such as cancer, diabetes, osteopetrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, heart disease, immune system disorders, blood disorders; the list goes on.
Worldwide, there are about 2 billion people suffering from various types of life threatening diseases such as cancer, diabetes, osteopetrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, heart disease, immune system disorders, blood disorders; the list goes on.
Although a wide assortment of methods are used to treat and cure these serious diseases, since the late 1980s, cord blood stem cells have increasingly been used to effectively treat a number of life threatening diseases.
When a baby is born, his or her umbilical cord is filled with a small amount of blood. This blood contains high numbers of special cells called stem cells. If you choose, this blood can be stored. It will then be used in the future to treat children or their family members with deadly diseases including Leukemia and Lymphoma. Often, this blood can be used to treat children when a donor cannot be found for a bone marrow transplant.
Put simply, the blood from your child’s umbilical cord could save a human life. Until recently, this blood with the potential to save lives was simply discarded as medical waste.
An infant’s cord blood could prove to be a life-saving treatment option if that child is born with a congenital heart defect, or later in life following a sudden and serious heart attack.
Why Cord Blood Stem Cells?
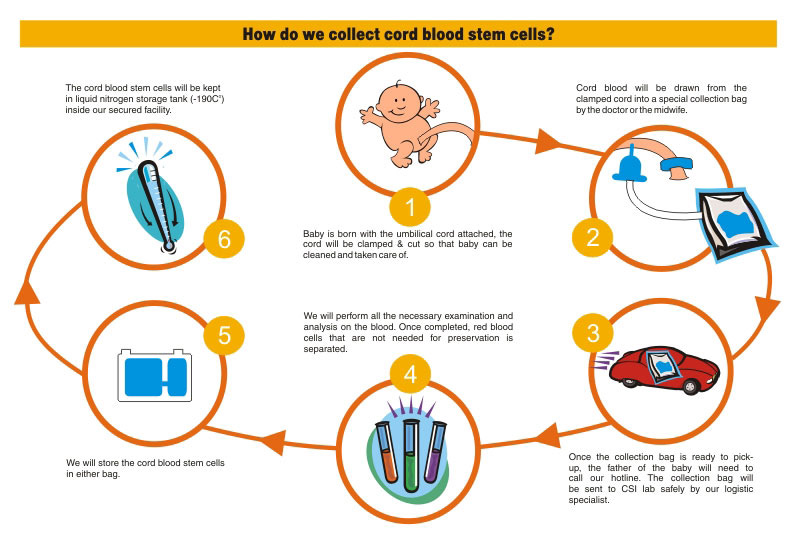
Cord blood stem cells offer several advantages over bone marrow stem cells and embryonic stem cells, including:
- Collection of cord blood stem cells poses no serious risks to either the baby or the mother because it is collected after birth.
- Unlike embryonic stem cells, umbilical cord blood is a non-controversial source of stem cells.
- With cord blood stem cells, the risk of viral infection is less.
- There is a significantly reduced risk of graft vs. host reaction.
- Cord blood stem cells not only occur in higher concentration than bone marrow stem cells, but they also have a higher capacity to replicate since they are harvested from the umbilical cord blood when they are very young, and, due to preservation, they do not age, hence their vitality is preserved.
While cord blood stem cell transplant therapy has many advantages, its use is somewhat limited because of the difficulty in finding a perfect match. Nevertheless, there are about 75 diseases that can be treated through the use of cord blood stem cells. These diseases can be segregated into congenital (present at birth) diseases and acquired diseases.
Cord Blood Stem Cell Types and Limitations
For the treatment of congenital diseases, the patient’s own cord blood cannot be used because the same disease also affects the stem cells located there. In such cases, cord blood stem cells from a sibling or an unrelated donor are used.
A cord blood stem cell transplant can be one of two types:
- Autologous transplantation, where the patient’s own cord blood stem cells are used in treatment.
- Allogeneic transplantation, where cord blood stem cells coming from a sibling or an unrelated donor are used.
Typically, the selection of the transplantation therapy depends upon several factors that differ from patient to patient.
What are the Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells Used For?

Stem cells from umbilical cord blood can be used to treat a wide variety of blood, bone, genetic, and immune system diseases in children, including:
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Adrenoleukodystrophy
- Krabbe’s Disease
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Osteopetrosis
- Cardiovascular disease
Many are considered life-saving procedures. Some of these diseases, such as Krabbe’s Disease, were deadly before the development of stem cell transplants. On rare occasions these procedures can be used to treat adults. The small amount of stem cells collected from each cord allows for transplants mostly in children. Research continues to increase the use of stem cells in adults and to treat many other diseases.
Scientists are still examining cord blood stem cells and perfecting how to use these stem cells in treatment. It is hoped and expected that, in the future, cord blood stem cells will be used to treat many other disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, heart disease, liver disease, muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease (a neurological illness), spinal cord injury and stroke.
What is Cord blood banking?
Cord blood banking means saving or storing the stem cells. To get these stem cells, your doctor will draw blood from the umbilical cord at the time of your baby’s birth. This blood is then dispatched to the company whose services you want to use. Here the stem cell’s are removed from the blood and stored particularly for the later use of your family.
All expectant parents must take an educated decision as to what is proper for them. Remember, storing your baby’s cord blood stem cells provides you an assurance to deal with future critical conditions. The charges and the advantages it offers about your family’s later health are just few of the points that should be considered when deciding. For more information, click here.
Source of information: http://www.womens-health.co.uk
Related Links
- Top 10 Biggest Pregnancy Fears
- New heart guidelines to stop newborn defects
- Approaches to Childbirth
- In touch with you baby
- The Stages of Labor & Delivery
- After the baby arrives
Disclaimer
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.