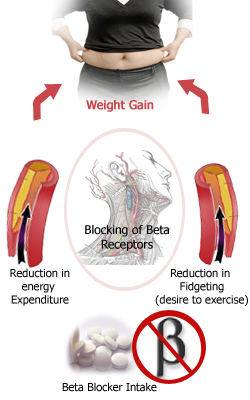
Studies have revealed that beta blockers cause a reduction in energy expenditure of four to nine percent, which rises to 12 percent in obese hypertensive persons thereby increasing chances of weight gain.
Beta blockers (sometimes written as β-blocker) is a class of drugs that ease the heart’s pumping action and widen the blood vessels. This therapy is used to lower a person’s blood pressure and heart rate and to treat angina. Beta-blockers slow down the heart beat, reduce the force of the heart muscle’s contractions, and decrease blood vessel contraction in the heart, brain, and the rest of the body.
Beta blockers, such as atenolol and propranolol, reduce the body’s ability to respond to insulin, causing high blood insulin levels that increase risk for weight gain. According to Sheldon. G. Sheps, hypertension specialist “The average weight gain is no more than 4 pounds (about 2 kilograms). Newer beta blockers, such as carvedilol (Coreg), don’t typically cause weight gain as a side effect”. Doctors aren’t sure exactly why some beta blockers cause weight gain. It could be that beta blockers slow your metabolism. Also, if you switch from taking a water pill (diuretic) to a beta blocker as a treatment for high blood pressure, you may gain a few pounds of weight that the diuretic kept off.
Effect of beta blockers on your body.
As mentioned,
 Beta blockers decrease the rate of heart beat, and hence blood pressure.
Beta blockers decrease the rate of heart beat, and hence blood pressure.- Availability of lower amounts of blood to the body means decrease in the availability of nutrients and oxygen to all the body cells. They also increase the oxidation of proteins.
- All these factors collectively results in the reduction of the rate of metabolism.
- A slow metabolism further leads to decrease in the consumption of calories.
- This is the first way that how beta blockers and weight gain are related to each other. As per studies, beta blockers cause a reduction in energy expenditure by 4-9%. This raises the percentage of weight gain by almost 11% in the patient who are on long term prescription of beta blockers.
- The second way involved is, beta blockers impart a feeling of tiredness and fatigue. This causes a marked reduction in fidgeting. Decreasing the desire to exercise or to do any kind of physical activity. This the another way that explains a relationship between beta blockers and weight gain.
- Thirdly, fat cells have beta receptors on their surfaces. The beta receptors play an important role in the metabolism of fat. Beta blockers block these beta receptors and interfere with the fat cells’ metabolic activities. Thus, the long term intake of beta blockers cause accumulation of body fat and decrease in the concentration of fat free tissue. This particularly causes accumulation of fat around the abdominal region. This is another way that establishes a relationship between beta blockers and weight gain.
In case, you are taking beta blocker, keep a close check on your weight. Check your weight everyday. If you happen to notice a gain of three or four pounds within a period of two or three days, you should inform your physician about it. Strictly, follow all the instructions and advices suggested by him. Following a low calorie diet and regularly involving yourself in physical activities will prove to be of great help.
In addition to causing weight gain, beta blockers like Lopressor have a number of other side effects such as fatigue, dizziness and difficulty breathing that could compromise your ability to effectively work out, further hampering your weight loss goals.
Beta Blockers and Exercise Constraints
 Beta blockers put a cap on the maximum heart rate and therefore, put a restriction on your exercise and stamina level. It may be difficult at the start, after you have started your first course of beta blockers to start exercising. Slowly you must learn to cope up with it. Understand the limits of your stamina, endurance and exercise accordingly.
Beta blockers put a cap on the maximum heart rate and therefore, put a restriction on your exercise and stamina level. It may be difficult at the start, after you have started your first course of beta blockers to start exercising. Slowly you must learn to cope up with it. Understand the limits of your stamina, endurance and exercise accordingly.
If you have been monitoring the degree of exertion achieved during a cardiovascular exercise routine by monitoring heart rate, you may have to consider measuring that in a different way, as your heart rate will not be a very good indicator any more, due to the threshold limit set by beta blockers. Consult your doctor and plan a different exercise regimen which is compatible with your modified condition.
A medication causes an artificial modification in natural body function and therefore, it is bound to cause imbalance somewhere.
How to lose weight with beta blockers
According to the American Heart Association, beta blockers are beneficial medications because they help to prevent heart attacks and stroke. By adopting the following lifestyle modification you can achieve considerable benefits:
- Eat five small meals per day. To lose weight while taking beta blockers you need to speed up your metabolism.
- Drink eight to ten glasses of pure water each day. Be sure you only drink purified water, rather than tap water.
- Take supplements in the morning. To combat the fatigue caused by your medications you will need to fight back with extra vitamins. Take an iron supplements and B-complex supplement with breakfast. You need 25 mg or iron per day and 50 mg of each of the B-vitamins each day.
- Exercise five days per week. People on heart medications of any kind need to work harder to lose weight because beta blockers and other medications slow down the heart rate. You can safely raise your heart rate with mild to moderate exercise each day.
In order to manage this side effect, the drug companies have developed newer beta blockers such as dilevalol, carvedilol and celiprolol that do not raise insulin levels and therefore do not increase a person’s chances of suffering heart attacks, diabetes and weight gain.
Disclaimer
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



