Washington State University researchers have found that people can manage chronic pain and reduce their reliance on opioids through an Internet-based program that teaches non-medical alternatives like increased physical activity, thinking more positively and dealing with emotions. Marian Wilson, an assistant professor in the College of Nursing, tracked 43 people with chronic … [Read more...]
Women Health News

Anabolic steroids has impact on memory: A Northumbria University Study
People using anabolic steroids to improve muscle growth and sporting performance are far more likely to experience issues with their memory, according to new research from Northumbria University. In some specialist gym user groups -- such as bodybuilders and weightlifters -- it is estimated that as many as 38% take steroids. Dr Tom Heffernan from the University's Department … [Read more...]
Life expectancy substantially lower with combination of diabetes and heart attack
In an analysis that included nearly 1.2 million participants and more than 135,000 deaths, mortality associated with a history of diabetes, stroke, or heart attack was similar for each condition, and the risk of death increased substantially with each additional condition a patient had, according to a study in the July 7 issue of JAMA. The prevalence of cardiometabolic … [Read more...]
Smartphones reduces ability to learn.: A Rice University Study
A yearlong study of first-time smartphone users by researchers at Rice University and the U.S. Air Force found that users felt smartphones were actually detrimental to their ability to learn. The research paper "You Can Lead a Horse to Water But You Cannot Make Him Learn: Smartphone Use in Higher Education" appeared in a recent edition of the British Journal of Educational … [Read more...]
Molecule linked to muscle fatigue and that enhances exercise tolerance: A Duke University Study
Everyone's muscles have different limits. While professional athletes can train for hours before feeling fatigued, others struggle to mow the lawn or climb stairs. No panacea exists to create an equal playing field, nor will one likely be discovered, but a new study from Duke University questions whether this limit can be nutritionally extended. The research appears July 7 in … [Read more...]
Treadmill workstations reduce neck, shoulder muscle pain: A McGill University Study
Office work will become much less of a pain in the neck if Julie Côté has her way. That`s because this kinesiology researcher who teaches at McGill University is interested in finding ways to reduce or even prevent the kinds of muscular and skeletal stresses and pains that will affect one in ten office workers at some point in their careers. "Even though office workers may not … [Read more...]
Bioengineers develop highly elastic biomaterial for better wound healing
A team of bioengineers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), led by Ali Khademhosseini, PhD, and Nasim Annabi, PhD, of the Biomedical Engineering Division, has developed a new protein-based gel that, when exposed to light, mimics many of the properties of elastic tissue, such as skin and blood vessels. In a paper published in Advanced Functional Materials, the research team … [Read more...]
Extreme Exercise linked to Blood Poisoning: The Australian Study
Researchers have discovered that extreme exercise can cause intestinal bacteria to leak into the bloodstream, leading to blood poisoning. Experts at Monash University monitored people participating in a range of extreme endurance events, including 24-hour ultra-marathons and multi-stage ultra-marathons, run on consecutive days. "Blood samples taken before and after the … [Read more...]
Talking therapy helps in chronic low back pain: A University of Royal Holloway London Study
New research from Royal Holloway, University of London has found that a new form of talking therapy is a credible and promising treatment for people with chronic low back pain who are also suffering from related psychological stress. Professor Tamar Pincus from the Department of Psychology also found that patients preferred a combination of talking therapy and physiotherapy … [Read more...]
Poor sleep is associated with negative mood in women with bipolar disorder: A Study
Poor sleep is associated with negative mood in women with bipolar disorder, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine and University of Michigan Medical School. Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that causes unusual shifts in mood, energy, activity levels and the ability to carry out day-to-day tasks. The condition is marked by extreme mood episodes … [Read more...]
Healthy diet linked to lower death rates: A Vanderbilt University Study
Eating a healthy diet was linked with a lower risk of dying from heart disease, stroke, cancer or other diseases among a population of low-income individuals living in the Southeastern U.S., according to research led by Vanderbilt University investigators. Nearly two-thirds of the participants in the study were African-American. The study by first author Danxia Yu, Ph.D., … [Read more...]
Too much vitamin A can be harmful: A Study
Although vitamin A supplementation can have profound health benefits when someone is deficient, new evidence is emerging to show that vitamin A supplementation above and beyond normal levels may have negative health consequences. A new research report published in the July 2015 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology may help to explain why too much vitamin A can be harmful. … [Read more...]
Sugary drinks linked to high death rate: A Tufts University Study
Consumption of sugary drinks may lead to an estimated 184,000 adult deaths each year worldwide, according to research. In the first detailed global report on the impact of sugar-sweetened beverages, researchers estimated deaths and disabilities from diabetes, heart disease, and cancers in 2010. In this analysis, sugar sweetened beverages were defined as any sugar-sweetened … [Read more...]
‘Drink when thirsty’ to avoid fatal drops in blood sodium levels during exercise: A Study
For hikers, football players, endurance athletes, and a growing range of elite and recreational exercisers, the best approach to preventing potentially serious reductions in blood sodium level is to drink when thirsty, according to an updated consensus statement on exercise-associated hyponatremia (EAH). The recommendations appear in the June issue of the Clinical Journal of … [Read more...]
Two migraine surgery techniques are highly effective: A Study
Two migraine surgery techniques targeting a specific "trigger site" are both highly effective in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine headaches, according to a randomized trial in the July issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). Patients with temporal-type migraine derive … [Read more...]
Impulsive or frustrated feeling can be checked by taking a short sleep: A University of Michigan Study
Taking a nap may be an effective strategy to counteract impulsive behavior and to boost tolerance for frustration, according to a University of Michigan study. It's becoming increasingly common for people, especially adults, to not sleep an entire night. This can negatively impair a person's attention span and memory, as well as contribute to fatigue. U-M researchers … [Read more...]
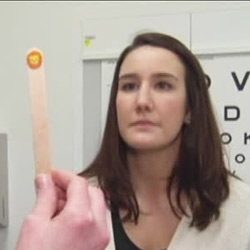
VOMS Test for Concussion
We’ve all heard a lot recently about the danger of concussions and how critically important it is to protect ourselves from repeated brain injury. Experts often use sophisticated equipment to measure concussion, but researchers in Pittsburgh have developed a simple test that is highly accurate, using items a doctor could carry in his pocket. 41-year-old Martin Rico was … [Read more...]
Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C has been updated
The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), in partnership with the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and in collaboration with the International Antiviral Society-USA (IAS-USA), created online Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C in 2014 to aid practitioners treating patients infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). … [Read more...]
Inactivity reduces muscle strength: A Danish study
A study has inferred that inactivity reduces muscle strength. New research reveals that it only takes two weeks of not using their legs for young people to lose a third of their muscular strength, leaving them on par with a person who is 40-50 years their senior. The Center for Healthy Aging and the Department of Biomedical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen conducted the … [Read more...]
Chronic disease and mental health issues linked to low-income African-Americans, Latinos and Hispanics: A University of California Study
A study has confirmed that chronic disease and mental health issues are linked to low-income African-Americans, Latinos and Hispanics. Chronic disease and mental health issues disproportionately affect low-income African-Americans, Latinos and Hispanics, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Two new studies by the UCLA Center for Culture, Trauma and … [Read more...]
Targeted drug delivery method for polycystic kidney disease: A University of California Study
A study has proved that a new targeted drug delivery method to slow the progression of polycystic kidney disease. For the 12 million people worldwide who suffer from polycystic kidney disease (PKD), an inherited disorder with no known cure, a new treatment option may be on the horizon. A targeted drug delivery method has been developed that could potentially slow the … [Read more...]
UTIs and STIs in women misdiagnosed half the time: A Study
A study has proved that UTIs and STIs in women are misdiagnosed half the time. Urinary tract and sexually transmitted infections in women are misdiagnosed by emergency departments nearly half the time, according to a paper in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, a publication of the American Society for Microbiology. These misdiagnoses result in overuse of antibiotics, and … [Read more...]
Diet and Acidity of urine may affect susceptibility to UTIs: A Washington University Study
A study has inferred that diet and acidity of urine may affect susceptibility to UTIs. The acidity of urine -- as well as the presence of small molecules related to diet -- may influence how well bacteria can grow in the urinary tract, a new study shows. The research, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, may have implications for treating urinary tract … [Read more...]
New nanotechnology drug to control blindness: Mexican Research
A new Mexican research has found a nanotechnology drug to control blindness. A innovative product in the form of droplets, reduces the cost of current medications, scientists say. It is a nanotechnology product, which works with last generation liposomes particles, concentrated in droplets, which function as a conveyor that wraps proteins or antibody fragments and allow its … [Read more...]
Medication can stop drug and alcohol addiction: A University of Texas Study
A study has established that medication can stop drug and alcohol addiction. Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have successfully stopped cocaine and alcohol addiction in experiments using a drug already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat high blood pressure. If the treatment is proven effective in humans, it would be the first of its … [Read more...]
Highly educated women stop smoking if the cost goes up: A Spanish Study
A study has concluded that highly educated women stop smoking if the cost goes up. Cigarette prices and images on cigarette packets have an impact on women in terms of continuing to smoke or quitting. In fact, less educated women are more responsive to pictorial labels on cigarette packets, as revealed by a study that has analysed, for the first time, the generation differences … [Read more...]
Increased anxiety associated with sitting down: A Study
A study has proved that there is increased anxiety associated with sitting down. Low energy activities that involve sitting down are associated with an increased risk of anxiety, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Public Health. These activities, which include watching TV, working at a computer or playing electronic games, are called sedentary … [Read more...]
Thick cortex could be key in Down syndrome: A Drexel University Study
A study has concluded that thick cortex could be the key to Down syndrome. The thickness of the brain's cerebral cortex could be a key to unlocking answers about intellectual development in youth with Down Syndrome. It could also provide new insights to why individuals with this genetic neurodevelopmental disorder are highly susceptible to early onset Alzheimer's Disease later … [Read more...]
Scientists identify amino acid that stops seizures: New Research
A study has found an amino acid that can stops seizures. An amino acid whose role in the body has been all but a mystery appears to act as a potent seizure inhibitor in mice, according to a study by researchers at Johns Hopkins. In a series of experiments, the amino acid D-leucine, found in many foods and certain bacteria, interrupted prolonged seizures, a serious condition … [Read more...]
People who practice yoga can control computers with their mind: A University of Minnesota Study
New research by biomedical engineers at the University of Minnesota shows that people who practice yoga and meditation long term can learn to control a computer with their minds faster and better than people with little or no yoga or meditation experience. The research could have major implications for treatments of people who are paralyzed or have neurodegenerative … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- …
- 96
- Next Page »