Over the past decade, studies have found that obesity and eating a high-fat, high-calorie diet are significant risk factors for many types of cancer. Now, a new study from Whitehead Institute and MIT's Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research reveals how a high-fat diet makes the cells of the intestinal lining more likely to become cancerous. The study of mice suggests … [Read more...]
Cancer News

Killing cancer cells with acid reflux: University of Central Florida Study
A University of Central Florida chemist has come up with a unique way to kill certain cancer cells -- give them acid reflux. Chemistry professor Kevin Belfield used a special salt to make cancer cells more acidic -- similar to the way greasy foods cause acid reflux in some people. He used a light-activated, acid-generating molecule to make the cells more acidic when exposed … [Read more...]
Low vitamin D predicts aggressive prostate cancer: Northwestern University Study
A new study provides a major link between low levels of vitamin D and aggressive prostate cancer. Northwestern Medicine research showed deficient vitamin D blood levels in men can predict aggressive prostate cancer identified at the time of surgery. The finding is important because it can offer guidance to men and their doctors who may be considering active surveillance, in … [Read more...]
Benefits of high-dose vitamin C for ovarian cancer patients: University of Kansas Study
Scientists at the University of Kansas Medical Center have determined that high doses of vitamin C, administered intravenously with traditional chemotherapy, helped kill cancer cells while reducing the toxic effects of chemotherapy for some cancer patients. By evaluating the therapy in cells, animals, and humans, the researchers found that a combination of infused vitamin C … [Read more...]
Risks of herbal medicines for cancer patients: An Israeli Study
Nearly two-thirds of the herbal medicines used by cancer patients in the Middle East have potential health risks, according to a new survey led by Assistant Professor Eran Ben-Arye, of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology. The study published in the journal Cancer concludes that herbal remedies such as turmeric may increase the toxic effects of certain chemotherapies, … [Read more...]
Link between exercise and improved prostate cancer outcomes: University of California Study
Men who walked at a fast pace prior to a prostate cancer diagnosis had more regularly shaped blood vessels in their prostate tumors compared with men who walked slowly, providing a potential explanation for why exercise is linked to improved outcomes for men with prostate cancer, according to results presented at the AACR-Prostate Cancer Foundation Conference on Advances in … [Read more...]
Antioxidant Supplementation Not Associated With Decreased Risk Of Prostate Cancer: A Study
Intakes of dietary or supplemental antioxidants were not associated with a decreased risk of prostate cancer among men in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial, according to a study in the February 15 issue of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute . The study did find that vitamin E and beta-carotene supplementation may be associated … [Read more...]
Cancer Tumors Shown To Consume Large Amounts Of Vitamin C: A Study
Researchers are cautious about cancer patients taking vitamin C supplements Researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center have found that cancer tumors consume large amounts of vitamin C. Their findings, which are reported in the September 15 issue of Cancer Research, may shed new light on the nutritional needs of tumors. "This study is the first to demonstrate … [Read more...]
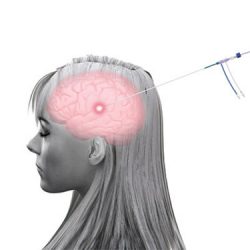
Visualase for Brain Tumors
For people with brain tumors, treatment usually involves invasive surgery as surgeons open portions of the skull to remove the cancer. If a tumor comes back, patients may begin to run out of options. A new FDA- approved device, also used to treat epilepsy, is now giving some patients another chance. Sixty-five-year-old Linda Fahey is writing a book, but weakness on her left … [Read more...]
Screen-detected prostate cancer overdiagnosis: A Study
Using a nomogram that incorporates age, Gleason score, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level at diagnosis, individual risks that a screen-detected prostate cancer has been overdiagnosed can be estimated, according to a new study published January 6 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute. The authors used a standard definition of overdiagnosis to refer to a … [Read more...]
Risk of prostate cancer overdiagnosis: University of Washington Study
Studies have found that prostate cancer is over-diagnosed in up to 42 percent of cases, prompting men to receive unnecessary treatment that can cause devastating side effects, including impotence and incontinence. Now, researchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the University of Washington have developed a personalized tool that can predict the likelihood of … [Read more...]
Development of a new type of anticancer agent
Microtubules, one component of a cell’s skeleton, are hollow tubes formed from the polymerization of α- and β-tubulin, which are themselves important structural proteins of the mitotic spindle that equally separates chromosomes during cell division. As such, several α/β-tubulin inhibitory agents are used as therapeutic drugs against cancer cells, which are undergoing vigorous … [Read more...]
Women with advanced-stage ovarian cancer can be cured: Women’s College Hospital Study
Up to half of women with advanced-stage ovarian cancer might be cured, compared to the current 20 per cent survival rate, argues Dr. Steven Narod, senior scientist at Women's College Research Institute, who calls for a new standard of treatment for women with late-stage ovarian cancer. Based on an analysis of existing evidence, published in an opinion article in the Nature … [Read more...]
A biomarker has been identified that predicts which stage II colon cancer patients may benefit from chemotherapy: Columbia University Study
A multicenter research team has identified a biomarker that predicts which stage II colon cancer patients may benefit from chemotherapy after surgery to prevent a recurrence of their disease. The study was published in the online edition of the New England Journal of Medicine. The majority of patients with stage II colon cancer--cancer that has grown into or through the … [Read more...]
Immunotherapy: Fighting Advanced Cancer
Patients with advanced cancers have new hope thanks to immunotherapy. It’s a therapy that trains the body’s own immune system to search out and destroy the cancer cells. Researchers say they’ve found an accurate way to screen the patients who may respond well to this treatment. For 25-year-old Stefanie Joho, her three sisters and parents are her world. Three years ago … [Read more...]
Lynparza for Advanced Ovarian Cancer
This year alone, 21,000 women will be diagnosed with ovarian cancer. Of those, 14,000 will die. Because the symptoms are so subtle, most women aren’t diagnosed until they are in the late stages of the disease. Now there is a new treatment that is bringing hope to some patients who have exhausted all other options. Fifty-seven-year-old Connie Scrivens is returning to normal … [Read more...]
Obesity and colorectal cancer linked: Thomas Jefferson University Study
Obesity has long been associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer, but the link has never been understood. Now, a research team led by investigators at Thomas Jefferson University has revealed the biological connection, and in the process, has identified an approved drug that might prevent development of the cancer. Their study is published in Cancer Research. In … [Read more...]
Prostate cancer is more aggressive in obese patients: A Study
Obesity has direct consequences on health and is associated with the onset of aggressive cancers, but the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon are little known. Researchers from the Institut de Pharmacologie et he Biologie Structurale (CNRS/Université Toulouse III -- Paul Sabatier) have recently elucidated one of these mechanisms in prostate cancer, one of the most common … [Read more...]
Gossypol a natural component found in the cotton plant can cure prostate cancer: University of Kansas Study
The genes that cause cancer are so tiny, yet so complex, that finding something to destroy or stop them is one of the top struggles for cancer researchers today. At The University of Kansas Cancer Center, understanding these microscopic processes and making drug discoveries is a priority in helping make the road for cancer patients easier and curbing recurrence. Liang Xu, … [Read more...]
Treatment for colorectal cancer discovered: National University of Singapore Study
Latest findings show that a small molecule drug combined with chemotherapy may deliver a synergistic benefit for colorectal cancer patients A study led by researchers from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS) has demonstrated the efficiency of a small molecule drug, PRIMA-1met, in inhibiting the growth of … [Read more...]
Most common gene mutation in Mediterranean countries linked to increased skin cancer: A Spanish Study
When Homo sapiens left Africa and had to adapt to less sunny climates, there was a mutation in one of the genes responsible for regulating the synthesis of melanin, the MC1R gene, which involved a discoloration of the skin. This discoloration allowed for better absorption of vitamin D, necessary for growth, but it also increased the risk of developing skin cancer in … [Read more...]
Link between nutrition and cancer: A study
In "Epigenetics: A New Link Between Nutrition and Cancer," a recent article from Nutrition and Cancer: An International Journal, a publication of Routledge, researchers explore the possible effects that diet can have on gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms. Explaining the impact of nutrition on epigenetic mechanisms may help to predict an individual's susceptibility to … [Read more...]
Reduction in Cancer fighting risk: Saint Louis University Study
In 1971, President Nixon funded research to wage a war on cancer, a long battle that we're still fighting today. While the last 40 years haven't brought us a cure, we have made some meaningful progress in developing tools and knowledge to take a bite out of our cancer risk. Mark Varvares, M.D., director of the Saint Louis University Cancer Center, suggests that lifestyle … [Read more...]
Melatonin shows potential to slow tumor growth in certain breast cancers: A Brazilian Study
An early stage study shows melatonin -- a hormone that regulates the body's sleep and awake cycles -- may have the potential to help slow the growth of certain breast cancer tumors, according to researchers from Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit and Foundation for Research Support of the State of São Paulo. The study, published online in the journal PLoS One, finds that … [Read more...]
Treating colon cancer with vitamin A: A Swiss Study
A leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide, colon cancer is famously resistant to treatment. There are many reasons for this, but one has to do with a group of persisting cancer cells in the colon that cause relapses. Conventional therapies against them are mostly ineffective. EPFL scientists have now identified a biological mechanism that can be exploited to counteract colon … [Read more...]
Patterns of cancer screening in Appalachian women: University of Kentucky Study
A new study by University of Kentucky researchers shows that women who never or rarely screen for breast cancer are also unlikely to receive screening for cervical cancer. The study also identified four key barriers independently associated with the lack of these cancer screenings in Appalachian women. Published in Women & Health, the study focused on six rural counties … [Read more...]
Number of cancer stem cells might not predict outcome in HPV-related oral cancers: Ohio State University Study
New research from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center -- Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC -- James) suggests that it may be the quality of cancer stem cells rather than their quantity that leads to better survival in certain patients with oral cancer. The researchers investigated cancer stem cell numbers in … [Read more...]
One in five women with ovarian cancer has inherited predisposition: Washington University Study
A new study conservatively estimates that one in five women with ovarian cancer has inherited genetic mutations that increase the risk of the disease, according to research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Most women in the study would have been unaware of a genetic predisposition to ovarian cancer because they didn't have strong family histories … [Read more...]
Psilocybin, found in magic mushrooms, decreased anxiety and depression in patients diagnosed with life-threatening cancer: A Study
A single dose of psilocybin, the major hallucinogenic component in magic mushrooms, induces long-lasting decreases in anxiety and depression in patients diagnosed with life-threatening cancer according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. Patients who receive a cancer diagnosis often develop debilitating symptoms … [Read more...]
Increased body mass index is associated with risk for ovarian cancer: University of Notre Dame Study
Ovarian cancer is a deadly disease, one that's hard to detect until it has progressed significantly. More than 75 percent of women diagnosed with ovarian cancer have metastasis at the time of diagnosis, resulting in a low five-year survival rate of less than 30 percent. A large number of studies have shown that an increased body mass index (BMI) is associated with a greater … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 37
- Next Page »