It is well documented that children with obese parents are at greater risk for obesity. In a new study, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, Cornell University, and Duke University looked at how different kinds of family associations affect obesity, specifically how sibling relationships affect a child’s weight. They not only found a correlation between parents and … [Read more...]
Alternative Health News

New compounds that could affect circadian rhythm uncovered: A Study
Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have discovered a surprising new role for a pair of compounds -- which have the potential to alter circadian rhythm, the complex physiological process that responds to a 24-hour cycle of light and dark and is present in most living things. At least one of these compounds could be developed as a … [Read more...]
Outdoor light has role in reducing short-sightedness in kids: Queensland University Study
Increasing exposure to outdoor light is the key to reducing the myopia (short-sightedness) epidemic in children, according to ground-breaking research by Australian optometrists. Optometrist and lead researcher on the project, Associate Professor Scott Read who is the director of research at QUT's School of Optometry and Vision Science, said children need to spend more than … [Read more...]
New cure for hepatitis C with 6 weeks: A German Study
A pilot study presented today found that all patients with acute HCV who were treated with a direct-acting antiviral treatment over a 'short-duration' of six weeks had undetectable HCV after a 12 week follow-up. The investigator-initiated study, presented at The International Liver CongressTM in Barcelona, Spain, demonstrated that the combination of sofosbuvir and ledipasvir … [Read more...]
Children with sweet tooth more likely to experience weight gain: University of Michigan Study
Some say there's always room for dessert -- but those who follow that motto young may be more likely to gain unhealthy weight, a new study suggests. Toddlers who reached for cookies over chips when their bellies were full had a higher risk of body fat increases, University of Michigan researchers report in the May issue of Pediatrics. "Eating in the absence of … [Read more...]
Most Americans pray for healing: Baylor University Study
Nearly nine of 10 Americans have relied upon healing prayer at some point in their lives, praying for others even more than for themselves, according to a study by a Baylor University epidemiologist. "The most surprising finding is that more than a quarter of all Americans have practiced laying on of hands -- and nearly one in five has done so on multiple occasions," said … [Read more...]
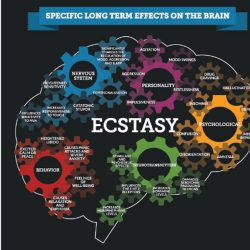
Effect of ecstasy on the brain: University of Liverpool Study
Researchers from the University of Liverpool have conducted a study examining the effect ecstasy has on different parts of the brain. Dr Carl Roberts and Dr Andrew Jones, from the University's Institute of Psychology, Health and Society, and Dr Cathy Montgomery from Liverpool John Moores University conducted an analysis of seven independent studies that used molecular … [Read more...]
Zika Virus Warnings
Could a trip out of the country compromise the health of your baby? A young mom takes the pros and cons of traveling in the days of the Zika virus into consideration. Like most young couples, Rhonda Spinks and her husband are thrilled to be expecting. Spinks told Ivanhoe, “This is our first baby and of course when it’s your first you’re extra cautious.” Spinks was … [Read more...]
Ddéjà vu: Texas A&M University Study
You walk into a room and suddenly your brain goes fuzzy with an overwhelming wave of familiarity -- although this is a totally new experience. Like something out of a sci-fi plot, it almost seems as if you've walked into the future. Chances are, you've experienced this situation, known as déjà vu, during your life. Déjà vu (French for 'already seen') occurs in approximately … [Read more...]
Once-a-day epilepsy drug may prevent seizures: A Swedish Study
A new study suggests that an epilepsy drug that can be taken once a day may control seizures as well as a drug that must be taken twice a day, according to a preliminary study released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 68th Annual Meeting in Vancouver, Canada, April 15 to 21, 2016. The study compared the once-a-day drug eslicarbazepine … [Read more...]
Bone marrow fat tissue secretes hormone that helps body stay healthy: University of Michigan Study
It has been known for its flavorful addition to soups and as a delicacy for dogs but bone marrow fat may also have untapped health benefits, new research finds. A University of Michigan-led study shows that the fat tissue in bone marrow is a significant source of the hormone adiponectin, which helps maintain insulin sensitivity, break down fat, and has been linked to … [Read more...]
Older adults are Facebook’s fastest growing demographic: A Study
Older adults, who are Facebook's fastest growing demographic, are joining the social network to stay connected and make new connections, just like college kids who joined the site decades ago, according to Penn State researchers. "Earlier studies suggest a positive relationship between bonding and bridging social capital and Facebook use among college students," said Eun Hwa … [Read more...]
Toothpaste ingredient that hardens teeth while sleeping: University of Queen Mary London Study
A new toothpaste ingredient which puts back the lost minerals from tooth enamel and helps prevent decay and treat sensitivity while you sleep is available online and from specialist dental distributors now. It is expected to be available through high street stores by the end of the year. The new BioMinF toothpaste ingredient provides a new tooth repair technology which will … [Read more...]
Treating Liver Cancer with Tiny Beads
Treating cancer that began in the liver or has spread to the liver can often involve months of chemotherapy and painful radiation treatments. But now there’s a new procedure that takes tiny beads that carry a high dose of radiation and sends them straight to the cancer. When Richard Dowling was diagnosed with liver cancer at 76, he figured doctors would focus more on his … [Read more...]
Seeing the light: Chemists create mimic of key vision protein
An artificial mimic of a key light-sensitive molecule has been made by scientists at the University of Bristol. The work, published in Science, could lead to new ways of building light-sensitive artificial cells. Professor Jonathan Clayden and colleagues in Bristol's School of Chemistry, along with collaborators at the Universities of Manchester and Hull, created an … [Read more...]
Tequila agave offers treatment for osteoporosis: A Mexican Study
A Mexican scientist has identified substances from the tequila plant that enhance absorption of calcium in the body. Apart from being the raw material for making a very traditional drink in Mexico, the blue variety of the Agave tequilana has substances capable of improving the absorption of calcium and magnesium, essential minerals to maintain bone health. This has been … [Read more...]
Infant-friendly flu vaccine developed with key protein: University of Missouri Study
According to the World Health Organization, influenza causes serious illness among millions of people each year, resulting in 250,000 to 500,000 deaths. Those most at risk include infants younger than six months, because they cannot be vaccinated against the disease. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri School of Medicine have identified a naturally occurring protein … [Read more...]
Mutation in APC2 gene causes Sotos features: A Study
Sotos syndrome is a congenital syndrome that is characterized by varying degrees of mental retardation and a large head circumference etc. It is known that 90% of Sotos syndrome patients have mutations in the NSD1 gene. This time, an international research group has revealed that mutation in the APC2 gene causes symptoms of Sotos syndrome related to the nervous system, from … [Read more...]
Collagen, heparan sulfate coatings alter cell proliferation and attachment: University of California Study
A group of researchers led by Dr. James Dunn out of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) are pleased to announce publication of their research in an upcoming issue of the journal TECHNOLOGY. The report, part of a thesis project of first author Christopher Walthers, Ph.D, was co-authored by Chase Lyall, M.S., Alireza Nazemi, M.S., and Puneet Rana, M.S. This paper … [Read more...]
Brain’s ‘amplifier’ compensates for lost inner ear function: Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Study
Researchers from Massachusetts Eye and Ear/Harvard Medical School have described, for the first time, the adult brain's ability to compensate for a near-complete loss of auditory nerve fibers that link the ear to the brain. The findings, published in the current issue of Neuron, suggest that the brain's natural plasticity can compensate for inner ear damage to bring sound … [Read more...]
Protein structure illuminates how viruses take over cells: Harvard Medical School Study
Using cutting-edge imaging technology, Salk Institute and Harvard Medical School researchers have determined the structure of a protein complex that lets viruses similar to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) establish permanent infections within their hosts. Contrary to previous assumptions, the newly detailed viral protein complex structure indicates that this type of … [Read more...]
Pathways of potent antibodies that fight HIV infection found: Duke University Study
One of the most crucial and elusive goals of an effective HIV vaccine is to stimulate antibodies that can attack the virus even as it relentlessly mutates. Now a research team, led by investigators at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute and the Vaccine Research Center of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), has tracked rare potent antibodies in an … [Read more...]
How ‘salt’ MRI scans could give a clearer picture of disease: University of Nottingham Study
MRI experts at The University of Nottingham win £1m grant to adapt scanning techniques to pick up sodium in the body. The research could lead to much more detailed MRI scans in the future with significant improvements to the diagnosis and treatment of many diseases. A novel technique to use the body's natural sodium (salt) content to provide a more detailed picture of tissue … [Read more...]
Trained technicians using CV software improved the accuracy and quality of LDCT scans: A Canadian Study
Trained technician screeners with assisted computer-aided nodule detection or computer vision (CV) screening workstations can efficiently and accurately review and triage abnormal low-dose computed topography (LDCT) scans for radiologist review. The National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST) reported that three annual low-dose computed topography (LDCT) scans, in … [Read more...]
Hormones causing children’s weight gain: Loyola University Study
The number of children who are obese remains alarmingly high in the U.S. and, unfortunately, diseases associated with obesity are on the rise. Worried about their overweight children, many parents wonder if other diagnoses, such as hypothyroidism, could be the reason behind their child's weight gain. But according to experts more often than not the underlying issues are more … [Read more...]
Nutrition education program improves preschoolers’ at-home consumption of vegetables, low-fat or fat-free milk: A Study
A nutrition education program in low-income child care centers can improve a child's at-home consumption of vegetables and low-fat/fat-free milk, according to a study by researchers from RTI International, Altarum Institute, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture. The study was supported by the USDA's Food and Nutrition Service. The study, published in the Journal of the … [Read more...]
New gene for severe childhood epilepsy identified: A Study
A European consortium of epilepsy researchers has reported the discovery of a new gene involved in severe childhood epilepsy. Using a novel combination of technologies, including trio exome sequencing of patient/parental DNA and genetic studies in the tiny larvae of zebrafish, the EuroEPINOMICS RES consortium found that mutations in the gene CHD2 are responsible for a subset of … [Read more...]
Evolocumab has no added benefit: A German Study
Evolocumab (trade name: Repatha) has been approved since July 2015 for two therapeutic indications: on the one hand, for hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia, and on the other, for homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. The drug is an option for patients whose cholesterol levels are not adequately lowered by diet and other drugs. The German Institute for Quality and … [Read more...]
Broccoli ingredient has positive influence on drug efficacy: University of Zurich Study
Certain foods can alter the activity of endogenous enzymes and thus influence the efficacy of drugs. It is well known, for example, that grapefruit has an adverse effect on a number of anti-arrhythmic and cholesterol-lowering drugs: it contains ingredients that inhibit an endogenous enzyme responsible for the degradation of certain medications in the liver. Consumption of … [Read more...]
MRI technique developed for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: UC San Diego School of Medicine Study
Between 5 and 8 million children in the United States have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), yet most cases go undiagnosed. To help address this issue, researchers at UC San Diego School of Medicine have developed a new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based technique to help clinicians and researchers better detect and evaluate NAFLD in children. The study is published … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 25
- Next Page »