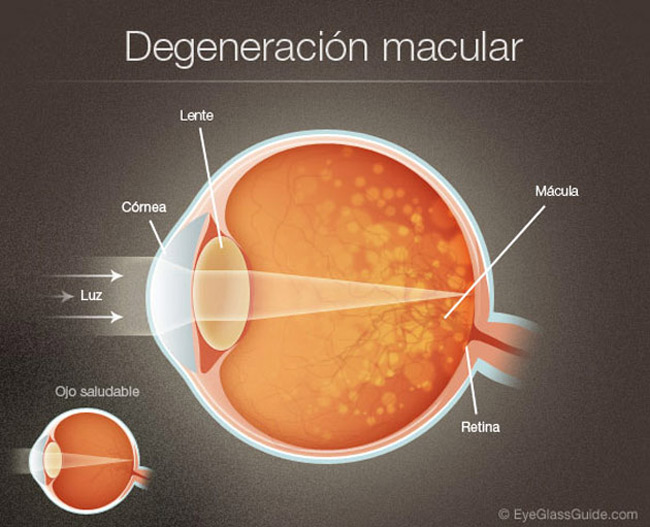
Macular degeneration is a breakdown of the crucial central portion of the retina that records the images we see and sends them via the optic nerve from the eye to the brain, called the macula.
This disease robs people of the central vision needed to see fine details directly in front of them recognize a familiar face across a room or read words on the printed page.
There are two types of Age-related macular degeneration (AMD):
- Dry and
- Wet.
Dry macular degeneration the more common, less destructive form occurs when deposits called drusen collect behind the retina. Wet AMD can pose a more rapid and serious threat to vision. With this type new blood vessels and scar tissue grow beneath the retina where they my leak blood or fluid and blur central vision. Only 10% of people with AMD have the wet type but it account for 90% of serve vision from the disease.

WHO’S AT RISK ?
Age is the biggest risk factor for developing AMD. Others include, a family history of AMD, cigarette smoking, long – term exposure to sunlight, hypertension and elevated levels of cholesterol. For unknown reasons women are more likely to develop AMD, than men.
WARRING SIGNS
Slightly blurry vision is the most common one. You may need more reading light and you may have trouble recognizing faces until you are very close to them. As dry AMD progresses you may see a blurred spot in the centre of your vision that gets bigger and darker over time.
The first warning sign of wet AMD may be straight lines that appear crooked or way.
However there may be no symptoms in the disease’s earliest stage. That’s why regular eye exams are so important.
If those who at risk for advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD) took daily supplements of antioxidant, vitamins and zinc, more than 300,000 people could avoid AMD-associated vision loss
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the condition is made by vision test and by examination of the retina with an ophthalmoscope. If there is a possibility of wet macular degeneration, then fluorescein angiography may be carried out to check for abnormal blood vessels.
CAN YOU PREVENT IT ?
A balanced diet consisting of plenty of fruits and vegetables can provide the nutrients found the be beneficial to the eyes specifically in relation to AMD. These include the antioxidant vitamins, lutein, vitamin E (found in nuts & leafy greens) and zinc (found in beef, milk, yogurt and eggs).
How do they work in preventing AMD? Free radicals molecules that can damage cells are formed as a by- product of metabolism and the macula has the right rate of metabolisms in the body. The macula is also high in polyunsaturated fatty acids which are especially susceptible to free – radical attack. Antioxidant can neutralize free radicals preventing them for harming healthy cells.
THE TREATMENT
There’s no cure for AMD. But, dry AMD develops slowly and most people are able to lead a normal life especially if the disease affect only one eye. Results of a well – designed U.S. clinical trial offered the first substantial hope of slowing the damage from macular degeneration. The national eye institute ‘s Age – Related Eye Disease Study (A R E D S) involved some 3.600 people with the disease. They took either a supplement containing zinc, one with antioxidant vitamins, mixture of both or a placebo. After six years, people with lots of drusen but good vision in both eyes and those with advanced macular degeneration in one year only had a 25 per cent lower risk of further damage.
The researches recommend that people with intermediate disease or with macular or with advanced macular degeneration in one eye should discuss with their doctor about taking a daily supplement of 500 milligrams of vitamin C, 400 milligrams of vitamin E, 15 milligrams of beta carotene, 80 milligrams of zinc as zinc oxide and 2 milligrams of copper as cupric oxide.
The wet form of macular degeneration is caused by the abnormal growth of fragile blood vessels in the retina that leak blood and cause damage to the light-sensitive photoreceptor cells. The new drug, called Macugen, works by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein that promotes blood vessel growth. Macugen has the potential for helping all patients with the wet form of the disease, whereas the currently approved treatment, photodynamic therapy, is only approved for patients that have a subtype of wet macular degeneration.
For wet AMD, 20 to 40 % of cases when they’re caught early can be treated with, laser surgery or with a new combination of a drug (verteporfin) and a laser therapy procedure called ocular photodynamic therapy.
To help you see better you doctor may recommend a variety of low – vision aids and strategies such as magnifiers, large-print books and bright lights.
Try eating more spinach. A study published in 1999 found that 13 out of 14 people with AMD who ate 1/2 cup of spinach four to seven times a week for a year hand improvements in their vision seven out of eight with serious vision distortion had improvements or complete resolution of their symptoms.