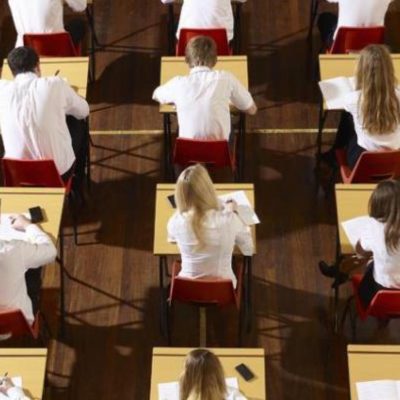
When college students learn specific techniques for managing stress and anxiety, their wellbeing improves across a range of measures and leads to better mental health, a new Yale study finds. The research team evaluated three classroom-based wellness training programs that incorporate breathing and emotional intelligence strategies, finding that two led to improvements in … [Read more...]
Can sleep protect us from forgetting old memories?
From lowering your risk of obesity and cardiovascular disease to improving your concentration and overall daily performance, sleep has been proven to play a critical role in our health. In a new study, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine report that sleep may also help people to learn continuously through their lifetime. Writing in the August … [Read more...]
Does eating fish protect our brains from air pollution?
Older women who eat more than one to two servings a week of baked or broiled fish or shellfish may consume enough omega-3 fatty acids to counteract the effects of air pollution on the brain, according to a new study published in the July 15, 2020, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Researchers found that among older women … [Read more...]
Loneliness Alters Your Brain’s Social Network
Social media sites aren't the only things that keep track of your social network -- your brain does, too. But loneliness alters how the brain represents relationships, according to new research published in JNeurosci. A brain region called the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) maintains a structured map of a person's social circles, based on closeness. People that struggle … [Read more...]
Study confirms ‘classic’ symptoms of COVID-19
A persistent cough and fever have been confirmed as the most prevalent symptoms associated with COVID-19, according to a major review of the scientific literature. Other major symptoms include fatigue, losing the ability to smell and difficulty in breathing. The study ratifies the list of symptoms listed by the World Health Organisation at the start of the … [Read more...]
Gut Bacteria may modify behavior in Worms, influencing Eating Habits
Gut bacteria are tiny but may play an out-sized role not only in the host animal's digestive health, but in their overall well-being. According to a new study in Nature, specific gut bacteria in the worm may modify the animal's behavior, directing its dining decisions. The research was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health. "We keep finding surprising roles for … [Read more...]
Physical activity prevents almost 4 million early deaths worldwide each year
At least 3.9 million early deaths are being averted worldwide every year by people being physically active, according to a new study published in The Lancet Global Health today by researchers at the Universities of Cambridge and Edinburgh. The team behind the study argue that too often we focus on the negative health consequences of poor levels of physical activity when we … [Read more...]
Coffee linked to lower body fat in women
Women who drink two or three cups of coffee a day have been found to have lower total body and abdominal fat than those who drink less, according to a new study published in The Journal of Nutrition. Researchers examined data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, organised by the Center for Disease Control (CDC) in the United States and looked at the … [Read more...]
Drinking sugary drinks daily may be linked to higher risk of CVD in women
Drinking one or more sugary beverages a day was associated with a nearly 20% greater likelihood of women having a cardiovascular disease compared to women who rarely or never drank sugary beverages, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association. In the large, ongoing … [Read more...]
More berries, apples and tea may have protective benefits against Alzheimer’s
Older adults who consumed small amounts of flavonoid-rich foods, such as berries, apples and tea, were two to four times more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease and related dementias over 20 years compared with people whose intake was higher, according to a new study led by scientists at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (USDA HNRCA) at Tufts … [Read more...]