In a small study, researchers found college athletes who contracted COVID-19 rarely had cardiac complications. Most had mild COVID symptoms that did not require treatment, and in a small percentage of those with abnormal cardiac testing, there was no evidence of heart damage on special imaging tests. All athletes returned to sports without any health concerns, according to new … [Read more...]
Brain Changes Following Traumatic Brain Injury Share Similarities With Alzheimer’s Disease
Brain changes in people with Alzheimer's disease and in those with mild traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) have significant similarities, a new USC study shows, suggesting new ways to identify patients at high risk for Alzheimer's. The findings appear this week in GeroScience. TBIs, which affect over 1.7 million Americans every year, are often followed by changes in brain … [Read more...]
Skin and Bones Repaired by Bioprinting During Surgery
Fixing traumatic injuries to the skin and bones of the face and skull is difficult because of the many layers of different types of tissues involved, but now, researchers have repaired such defects in a rat model using bioprinting during surgery, and their work may lead to faster and better methods of healing skin and bones. "This work is clinically significant," said … [Read more...]
DHA Supplement may Offset Impact of Maternal Stress on Unborn Males
Neurodevelopmental disorders like autism and schizophrenia disproportionately affect males and are directly linked to early life adversity caused by maternal stress and other factors, which might be impacted by nutrition. But the underlying reasons for these male-specific impacts are not well understood. Researchers from the University of Missouri School of Medicine and the MU … [Read more...]
Parkinson’s, Cancer, Type 2 Diabetes Share a Key Element That Drives Disease
When cells are stressed, chemical alarms go off, setting in motion a flurry of activity that protects the cell's most important players. During the rush, a protein called Parkin hurries to protect the mitochondria, the power stations that generate energy for the cell. Now Salk researchers have discovered a direct link between a master sensor of cell stress and Parkin itself. … [Read more...]
Artificial Intelligence Could ‘Crack The Language of Cancer and Alzheimer’s’
Powerful algorithms used by Netflix, Amazon and Facebook can 'predict' the biological language of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, scientists have found. Big data produced during decades of research was fed into a computer language model to see if artificial intelligence can make more advanced discoveries than humans. Academics based at St John's … [Read more...]
Cells Burn More Calories After Just One Bout of Moderate Aerobic Exercise, OSU Study Finds
In a recent study testing the effects of exercise on overall metabolism, researchers at Oregon State University found that even a single session of moderate aerobic exercise makes a difference in the cells of otherwise sedentary people. Mitochondria are the part of the cell responsible for the biological process of respiration, which turns fuels such as sugars and fats into … [Read more...]
Eating Processed Meat Could Increase Dementia Risk, Researchers Say
Scientists from the University's Nutritional Epidemiology Group used data from 500,000 people, discovering that consuming a 25g serving of processed meat a day, the equivalent to one rasher of bacon, is associated with a 44% increased risk of developing the disease. But their findings also show eating some unprocessed red meat, such as beef, pork or veal, could be protective, … [Read more...]
Exercise During Pregnancy may Save Kids from Health Problems as Adults
Exercise during pregnancy may let mothers significantly reduce their children's chances of developing diabetes and other metabolic diseases later in life, new research suggests. A study in lab mice has found that maternal exercise during pregnancy prevented the transmission of metabolic diseases from an obese parent -- either mother or father -- to child. If the finding holds … [Read more...]
For Better Migraine Treatment, Try Adding Some Downward Dogs
Adding yoga to your regularly prescribed migraine treatment may be better than medication alone, according to a study published in the May 6, 2020, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The new research suggests yoga may help people with migraines have headaches that happen less often, don't last as long and are less … [Read more...]
Bacteria may Aid Anti-Cancer Immune Response
Cancer immunotherapy may get a boost from an unexpected direction: bacteria residing within tumor cells. In a new study published in Nature, researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science and their collaborators have discovered that the immune system "sees" these bacteria and shown they can be harnessed to provoke an immune reaction against the tumor. The study may also help … [Read more...]
Satiety factor Associated with prolonged exercise
A drug that helps us to eat less could help the more than 650 million people around the world who live with obesity. One of the emerging drug candidates that interest researchers is the hormone GDF15 that, when given to rodents, lowers their appetite and body weight. New research from the University of Copenhagen finds that the body produces large amounts GDF15 during extended … [Read more...]
Pregnant women pass along protective COVID antibodies to their babies
Antibodies that guard against COVID-19 can transfer from mothers to babies while in the womb, according to a new study from Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian researchers published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. This discovery, published Jan. 22, adds to growing evidence that suggests that pregnant women who generate protective … [Read more...]
Toddler sleep patterns Significant
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule for a toddler can be one of the most challenging aspects of child rearing, but it also may be one of the most important. Research findings from a team including Lauren Covington, an assistant professor in the University of Delaware School of Nursing, suggest that children with inconsistent sleep schedules have higher body mass index … [Read more...]
Deciphering the genetics behind eating disorders
Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder are the three main eating disorders that 4 out of in 10 individuals living in Western Europe will experience at some point in their lives. In recent years, studies on the genetic basis of anorexia nervosa have highlighted the existence of predisposing genetic markers, which are shared with other psychiatric … [Read more...]
The right ‘5-a-day’ mix is 2 fruit and 3 vegetable servings for longer life
Studies representing nearly 2 million adults worldwide show that eating about five daily servings of fruits and vegetables, in which 2 are fruits and 3 are vegetables, is likely the optimal amount for a longer life, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation. Diets rich in fruits and vegetables help reduce … [Read more...]
Swapping alpha cells for beta cells to treat diabetes
Blocking cell receptors for glucagon, the counter-hormone to insulin, cured mouse models of diabetes by converting glucagon-producing cells into insulin producers instead, a team led by UT Southwestern reports in a new study. The findings, published online in PNAS, could offer a new way to treat both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes in people. More than 34 million Americans have … [Read more...]
Future of Immunotherapy could be ‘off-the-shelf’ treatments
In a new commentary for the journal Science, an associate vice president for research at The University of Texas at Arlington argues that emerging protein-based immunotherapy could lead to highly effective "off-the-shelf" cancer treatments for more patients. Jon Weidanz, who also is a professor in the College of Nursing and Health Innovation at UTA, is the author of a … [Read more...]
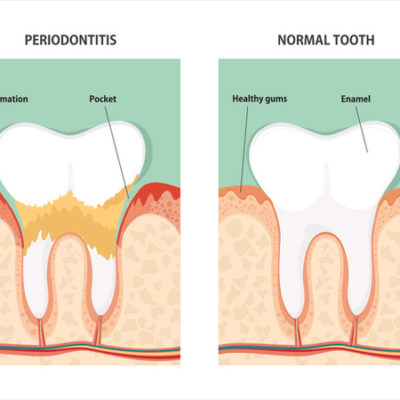
Dental experts discover biological imbalance is the link between gum and kidney disease
An imbalance of the body's oxygen producing free radicals and its antioxidant cells could be the reason why gum disease and chronic kidney disease affect each other, a new study led by the University of Birmingham has found. Periodontitis -- or gum disease -- is a common, inflammatory disease which causes bleeding gums, wobbly or drifting teeth and can eventually result in … [Read more...]
Sweat, bleach and gym air quality: Chemical reactions make new airborne chemicals
One sweaty, huffing, exercising person emits as many chemicals from their body as up to five sedentary people, according to a new University of Colorado Boulder study. And notably, those human emissions, including amino acids from sweat or acetone from breath, chemically combine with bleach cleaners to form new airborne chemicals with unknown impacts to indoor air … [Read more...]
Researchers Urge Priority Vaccination for Individuals with Diabetes
Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers have discovered individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes infected with COVID-19 are three times more likely to have a severe illness or require hospitalization compared with people without diabetes. Because of this amplified impact, they are urging policymakers to prioritize these individuals for COVID-19 vaccination. … [Read more...]
Study Connects Diabetes, Air Pollution to Interstitial Lung Disease
People with pre-diabetes or diabetes who live in ozone-polluted areas may have an increased risk for an irreversible disease with a high mortality rate. A new study published in the Environmental Health Perspectives connects insulin resistance and repetitive ozone exposure to the development of interstitial lung disease. "Our findings are especially important today as … [Read more...]
Healthy Muscles: a Carrot on a String for Healthy Lungs
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease caused by long-term inhalation of harmful gases such as cigarette smoke. Scientists have recognized deterioration of muscle tissue, known as, as a secondary effect of damaged lungs. This frailty makes it difficult for individuals to move around and exercise, which is turn worsens the state of their lungs, causing an … [Read more...]
Genetic differences in body fat shape men and women’s health risks
New research is revealing how genetic differences in the fat in men's and women's bodies affect the diseases each sex is likely to get. University of Virginia researchers Mete Civelek, PhD, Warren Anderson, PhD, and their collaborators have determined that differences in fat storage and formation in men and women strongly affect the activity of 162 different genes found in … [Read more...]
How changing the stem cell response to inflammation may reverse periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a serious infection that affects nearly 50 percent of Americans aged 30 years and older. If left unchecked, periodontal disease can destroy the jawbone and lead to tooth loss. The disease is also associated with higher risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The current treatment for periodontal disease involves … [Read more...]
Estrogen may Lessen Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms in Women, study finds
Why are men at greater risk than women for more severe symptoms and worse outcomes from COVID-19 regardless of age? In an effort to understand why this occurs, scientists at Wake Forest School of Medicine conducted a review of published preclinical data on sex-specific hormone activity, especially estrogen. The review is published in the September online issue of the … [Read more...]
Vitamin D Deficiency may Raise Risk of Getting COVID-19, study finds
In a retrospective study of patients tested for COVID-19, researchers at the University of Chicago Medicine found an association between vitamin D deficiency and the likelihood of becoming infected with the coronavirus. "Vitamin D is important to the function of the immune system and vitamin D supplements have previously been shown to lower the risk of viral respiratory … [Read more...]
Targeted Drug found Effective in Patients who have Lung Cancer with Certain Mutations
A targeted therapy called capmatinib can provide significant benefits to patients who have advanced lung cancer with specific gene mutations, according to recently published results from a phase two clinical trial. The trial, which is published in the New England Journal of Medicine, was conducted by an international team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital … [Read more...]
Rubbing skin Activates itch-relief Neural Pathway
Stop scratching: rubbing skin activates an anti-itch pathway in the spinal cord, according to research in mice recently published in JNeurosci. It can be hard to resist the relief of scratching an itch, even though scratching damages skin, especially in sensitive areas like the eyes. But stroking can relieve an itch, too. Sakai et al. investigated the neural pathway … [Read more...]
Children use both brain hemispheres to understand language, unlike adults
Infants and young children have brain with a superpower, of sorts, say Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists. Whereas adults process most discrete neural tasks in specific areas in one or the other of their brain's two hemispheres, youngsters use both the right and left hemispheres to do the same task. The finding suggests a possible reason why children appear to … [Read more...]