One-minute, short bursts of high-intensity interval training for 19 minutes may be more effective for improving fitness among people six months or more after a stroke than traditional, 20-30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise sessions, according to research published today in Stroke, the peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the … [Read more...]
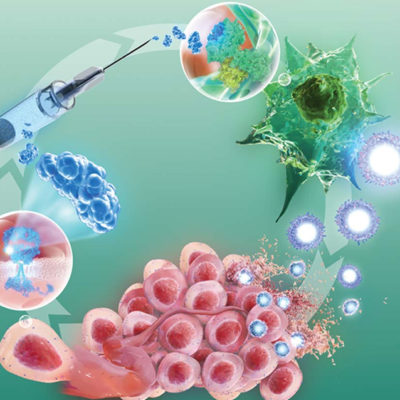
Why Cancer Immunotherapies don’t Work for Everyone
Why cancer immunotherapies don't work for everyone (cancer) The study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Cell Reports, sheds light on why immunotherapy treatments don't work for all people or all diseases. For example, certain types of cancers -- including colon, pancreatic, prostate and brain cancers -- have stubbornly resisted immunotherapy. And while breast, … [Read more...]
Is There a Link Between Migraine and Breast Cancer Risk?
Researchers estimate that between 14-15% of the world’s populationTrusted Source experience migraine — a neurological disorderTrusted Source that causes severe headaches and other symptoms that can impact a person’s daily life. Previous studies have linked migraine attacks to an increased risk for other conditions, including strokeTrusted Source, high blood pressureTrusted … [Read more...]
Target Protein For Diabetes Drug Linked to Reduced Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease
Mechanisms associated with a particular diabetes drug can also help to protect against Alzheimer's disease, a study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and published in Neurology reports. The results indicate that the drug's target protein can be an interesting candidate for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease is becoming increasingly … [Read more...]
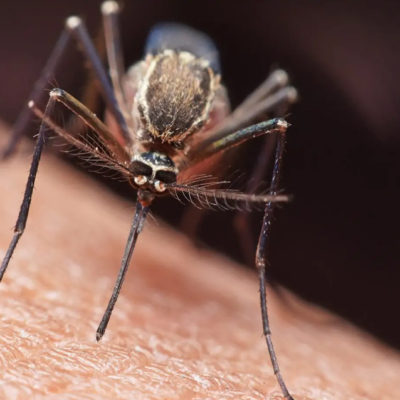
New Insights into Immune Responses to Malaria
Advanced technologies have been used to solve a long-standing mystery about why some people develop serious illness when they are infected with the malaria parasite, while others carry the infection asymptomatically. An international team used mass cytometry -- an in-depth way of characterising individual cells -- and machine learning to discover 'immune signatures' … [Read more...]
Babies at Risk for Diabetes may have Microbiota Restored
Newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because they were given antibiotics may have their gut microorganisms restored with a maternal fecal transplant, according to a Rutgers study. The study, which involved genetic analysis of mice, appears in the journal Cell Host & Microbe. The findings suggest that newborns at risk for Type 1 diabetes because their microbiome -- the … [Read more...]
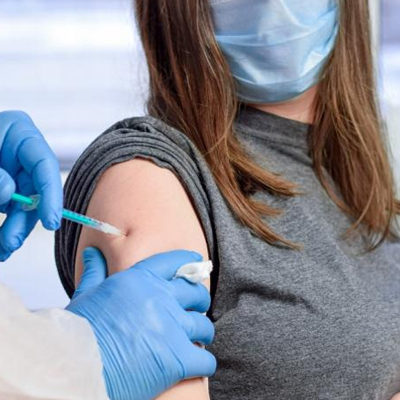
COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines are Immunogenic in Pregnant and Lactating Women, Study Finds
Pregnant women with symptomatic COVID-19 have a higher risk of intensive care unit admissions, mechanical ventilation and death compared to non-pregnant reproductive age women. Increases in preterm birth and still birth have also been observed in pregnancies complicated by the viral infection. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended that people who are … [Read more...]
Leg Muscle Action Assists Blood Flow Independently of Age
Chronic lower-limb edema (CLE) -- the permanent accumulation of fluid in the leg -- often occurs in elderly people. The condition leads to various physical and mental problems, including difficulty in walking or moving, fatigue and anxiety. One cause of CLE is the lack of physical activity, which is associated with a decrease in muscle pump action. The latter refers to the leg … [Read more...]
Recreating the earliest stages of life
In their effort to understand the very earliest stages of life and how they can go wrong, scientists are confronted with ethical issues surrounding the use of human embryos. The use of animal embryos is also subject to restrictions rooted in ethical considerations. To overcome these limitations, scientists have been trying to recreate early embryos using stem cells. One of … [Read more...]
Diets Rich in Nitrates from Vegetables Improve Muscle Function
Diets rich in nitrates from vegetables improve muscle function, according to a study published in the Journal of Nutrition. In 3,759 participants in the Australian Diabetes, Obesity, and Lifestyle Study (AusDiab), those with the highest nitrate consumption, mainly from vegetable sources, performed with more strength and speed in the physical tests when compared to those who ate … [Read more...]
Exercise During Pregnancy may Save Kids from Health Problems as Adults
Exercise during pregnancy may let mothers significantly reduce their children's chances of developing diabetes and other metabolic diseases later in life, new research suggests. A study in lab mice has found that maternal exercise during pregnancy prevented the transmission of metabolic diseases from an obese parent -- either mother or father -- to child. If the finding holds … [Read more...]
Pregnant women pass along protective COVID antibodies to their babies
Antibodies that guard against COVID-19 can transfer from mothers to babies while in the womb, according to a new study from Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian researchers published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. This discovery, published Jan. 22, adds to growing evidence that suggests that pregnant women who generate protective … [Read more...]
Deciphering the genetics behind eating disorders
Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder are the three main eating disorders that 4 out of in 10 individuals living in Western Europe will experience at some point in their lives. In recent years, studies on the genetic basis of anorexia nervosa have highlighted the existence of predisposing genetic markers, which are shared with other psychiatric … [Read more...]
Dieting and weight worries on rise in Teenagers
Significantly higher numbers of Generation Z boys and girls in the UK are dieting to lose weight, and are likely to overestimate their own weight, finds a new UCL-led study. The research, published in JAMA Pediatrics, found that girls who are trying to lose weight are also more likely to experience depressive symptoms than in previous years. In 2015, 42% of 14-year-old … [Read more...]