Pregnancy brings about many changes to a woman’s body. One of the more intriguing factor is a decrease in the T helper cells, resulting in a state of relative immuno-suppression. The T helper cells (Th cells) are a type of T cell that play an important role in the immune system, particularly in the adaptive immune system. They help the activity of other immune cells by releasing T cell cytokines. These cells help, suppress or regulate immune responses. They are essential in B cell antibody class switching, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages.

- Complications from pneumonia, are increased during pregnancy. You should avoid it as best you can if you are pregnant. There are a few things you can do to prevent getting pneumonia. To prevent getting the infection during your pregnancy, you should make sure you’re all caught up on your influenza vaccinations before you conceive. If you come down with any type of respiratory illness during your pregnancy, even a simple cough, monitor it closely. If it lingers in your lungs too long, it could cause pneumonia. If your cough is still around a week after your cold has subsided, see your doctor right away. You should also stay healthy in general. Washing your hands frequently, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet can also help prevent the infection. Avoid interaction with people who have cough.
- Increases in mortality related to influenza infection. Flu typically starts with a fever, achiness, and fatigue, followed by cold symptoms, such as a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat, cough, chills. You may have diarrhea or vomiting as well. Pregnant woman with flu also have a greater chance for serious problems for their unborn baby, including premature labor and delivery. In order to handle flu, treat any fever right away. Acetaminophen is the recommended treatment for fever when you’re pregnant. Drink plenty of fluids. Let your doctor decide whether you need antiviral drugs. Antiviral drugs are prescription pills, liquids, or inhalers that fight flu by keeping the germs from growing in your body. These medicines can make you feel better faster and make your symptoms milder. Antivirals work best when started within two days after symptoms begin, but they may be given to very sick or high risk people (such as moms-to-be) even after 48 hours.
- the risk for dissemination of coccidioidomycosis (valley fever). An infection caused when the spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis enter your body through the lungs. As a preventive measure, take care of your health to keep the disease in the benign pulmonary form. Preventing AIDS or other causes of immune system damage will usually prevent the more severe forms of the disease. People with immune problems (such as AIDS patients and those who are on drugs that suppress the immune system) should avoid travel to areas where this fungus is found, if they want to reduce their risk of getting this rare, chronic disorder.
|
Commonly used indicators to judge the severity of coccidioidomycosis (valley fever) include:
|
Other physiologic changes predispose the pregnant woman to certain disease processes.
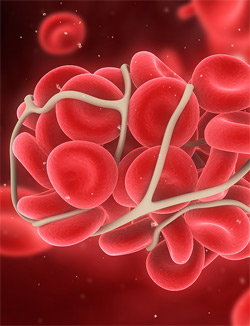 Hypercoagulability associated with pregnancy results in a marked increase in the incidence ofthromboembolic disease. Pregnancy itself is a factor of hypercoagulability (pregnancy-induced hypercoagulability), as a physiologically adaptive mechanism to prevent post partum bleeding. However, when combined with an additional underlying hypercoagulable states, the risk of thrombosis or embolism may become substantial. This disorder is common cause of death in pregnant women. In thromboembolic disorders, blood clots (thrombi) form in blood vessels. An embolus is a blood clot that travels through the bloodstream and blocks an artery. Successful pregnancies require an even balance of coagulation and fibrinolysis, in order to secure stabilization of the basal plate as well as adequate placental perfusion.
Hypercoagulability associated with pregnancy results in a marked increase in the incidence ofthromboembolic disease. Pregnancy itself is a factor of hypercoagulability (pregnancy-induced hypercoagulability), as a physiologically adaptive mechanism to prevent post partum bleeding. However, when combined with an additional underlying hypercoagulable states, the risk of thrombosis or embolism may become substantial. This disorder is common cause of death in pregnant women. In thromboembolic disorders, blood clots (thrombi) form in blood vessels. An embolus is a blood clot that travels through the bloodstream and blocks an artery. Successful pregnancies require an even balance of coagulation and fibrinolysis, in order to secure stabilization of the basal plate as well as adequate placental perfusion.- Although rare, pregnancy is also associated with other embolic phenomena including amniotic fluid embolism, air embolism, and trophoblastic embolism. Amniotic fluid embolism or AFE is a rare and incompletely understood obstetric emergency in which amniotic fluid, fetal cells, hair, or other debris enters the mother’s blood stream via the placental bed of the uterus and trigger an allergic reaction. This reaction then results in cardiorespiratory (heart and lung) collapse and coagulopathy. Sometimes, air bubbles enter a vein or artery and block it. These air bubbles can travel to your brain, heart, or lungs and cause a heart attack, stroke, or respiratory failure or air embolism.
- Because of the increases in intravascular volume and cardiac output that occur in pregnancy, women with underlying structural heart disease will frequently present for the first time or have an exacerbation of their disease. This is especially true of mitral stenosis. The mitral valve separates the upper and lower chambers on the left side of the heart. Stenosis is a condition in which the valve does not open fully, restricting blood flow. Mitral stenosis is a disorder in which the mitral valve does not open fully.
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy (PC) can occur, and for the majority of patients, the heart remains damaged for life. PC is a rare disorder in which a weakened heart is diagnosed within the final month of pregnancy or within 5 months after delivery. The damage weakens the heart muscle and causes the heart to become enlarged. As a result, the heart can’t pump blood properly throughout the rest of the body. According to the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, this heart condition affects about one in every 3,000 to 4,000 women each year. Women are diagnosed during the last month of their pregnancies or within five months of delivery.
- Finally, although uncommon, lymphangioleiomyomatosis will often present or become exacerbated during pregnancy. Patients with this disorder need to be counseled concerning the increased risk associated with pregnancy. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, a multisystem disease characterized by cystic lung lesions can result in respiratory failure and is considered to be sex hormones related. No effective treatment for lymphangioleiomyomatosis is currently available.
Note:
- Infants are unable to receive the influenza vaccine until they are 6 months of age. An effective way of reducing influenza for young babies is to vaccinate the pregnant woman. Passive transfer of antibodies to the fetus offers significant short term protection to the baby. Pregnancy vaccination reduces the risk of influenza in infants less than 6 months of age by more than 90%.
References:
Disclaimer
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



