Supplement Guidelines
In addition to eating a proper diet, you should also take dietary supplements to make sure that any nutrients you lose due to sweating or training are replenished.
Nutrients and their intake
The following tables will help guide you in selecting the
supplements appropriate for you. The first table lists the nutrients
recommended for bodybuilders, as well as the range of intake for
each nutrient. Note that within the ranges of intake, the lower
amounts are for smaller individuals and the lower-activity days,
while the higher amounts are for larger individuals and
higher-activity days.
| Nutrient | Range of Intake |
| Vitamin A | 8,000 - 16,000 IU |
| Beta Carotene | 20,000 - 30,000 IU |
| Vitamin B1 | 30 - 120 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 30 - 120 mg |
| Vitamin B3 | 40 - 80 mg |
| Vitamin B5 | 20 - 100 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 20 - 80 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 12 - 120 mcg |
| Biotin | 125 - 175 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 800 - 2,000 mg |
| Vitamin D | 400 - 800 IU |
| Vitamin E | 200 - 600 IU |
| Vitamin K | 60 - 160 mcg. |
| Boron | 2 - 8 mg |
| Calcium | 200 - 500 mcg |
| Iron | 15 - 50 mg |
| Magnesium | 250 - 650 mg |
| Manganese | 12 - 35 mg |
| Potassium | 50 - 1,000 mg |
| Selenium | 100 - 200 mcg |
| Zinc | 15 - 50 mg |
CREATINE: one of the hottest sports supplement
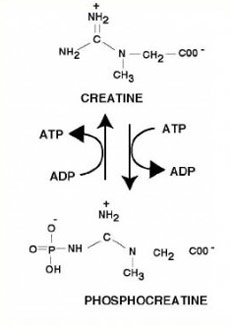 The
aim of this article is simply to inform the reader of the
basic principles and foundations behind creatine and its
supplementation. Its popularity is evident and likely a result of
the fact that, short of macronutrients, it is one of the most
researched exercise nutrition supplements to date; this compound
actually has been shown in well-controlled scientific studies to be
quite effective in producing desired results, unlike many, many
available to the unwary athlete these days.
The
aim of this article is simply to inform the reader of the
basic principles and foundations behind creatine and its
supplementation. Its popularity is evident and likely a result of
the fact that, short of macronutrients, it is one of the most
researched exercise nutrition supplements to date; this compound
actually has been shown in well-controlled scientific studies to be
quite effective in producing desired results, unlike many, many
available to the unwary athlete these days.
click here for more on creatine...

